The built-in SMBShare PowerShell module allows you to create, configure and manage shared network folders in Windows. In this article, we will look at how to manage file shares (SMB network folders) using PowerShell. You may use these examples to quickly and easily manage your SMB file servers and shared folders in different automation scenarios.
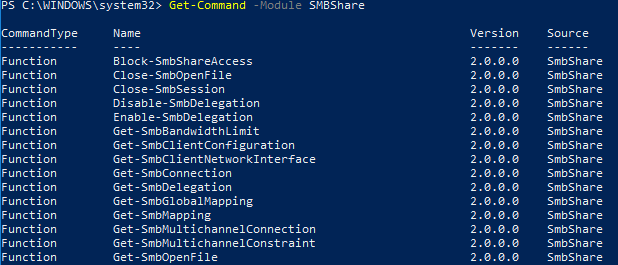
The SMBShare module contains 42 PowerShell cmdlets to manage shared network folders. You can display the full list of cmdlets in the module:
Get-Command -Module SMBShare
In order to display the current configuration of your Windows SMB server:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration
AnnounceComment : AnnounceServer : False AsynchronousCredits : 64 AuditSmb1Access : False AutoDisconnectTimeout : 15 AutoShareServer : True AutoShareWorkstation : True CachedOpenLimit : 10 DurableHandleV2TimeoutInSeconds : 180 EnableAuthenticateUserSharing : False EnableDownlevelTimewarp : False EnableForcedLogoff : True EnableLeasing : True EnableMultiChannel : True EnableOplocks : True EnableSecuritySignature : False EnableSMB1Protocol : True EnableSMB2Protocol : True EnableStrictNameChecking : True EncryptData : False IrpStackSize : 15 KeepAliveTime : 2 MaxChannelPerSession : 32 MaxMpxCount : 50 MaxSessionPerConnection : 16384 MaxThreadsPerQueue : 20 MaxWorkItems : 1 NullSessionPipes : NullSessionShares : OplockBreakWait : 35 PendingClientTimeoutInSeconds : 120 RejectUnencryptedAccess : True RequireSecuritySignature : False ServerHidden : True Smb2CreditsMax : 2048 Smb2CreditsMin : 128 SmbServerNameHardeningLevel : 0 TreatHostAsStableStorage : False ValidateAliasNotCircular : True ValidateShareScope : True ValidateShareScopeNotAliased : True ValidateTargetName : True
You can change SMB server options using the Set-SmbServerConfiguration cmdlet.
For example, to disable the legacy SMB 1 protocol, run the command below:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false -Force
To display a list of SMB protocol versions used by active clients to connect to file shares on current SMB file server:
Get-SmbConnection
To set bandwidth limits for SMB file traffic, you may configure the QoS policy for your SMB server (How to configure SMB bandwidth limits?). For example, the command below will limit the maximum bandwidth for SMB traffic to 10 MB:
Set-SmbBandwidthLimit -Category Default -BytesPerSecond 10MB
Creating a Shared Folder onWindows with PowerShell
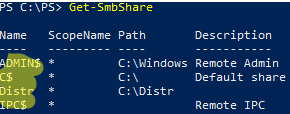
To display a list of shared folders available on a computer, run this command:
Get-SmbShare
You can see several administrative shares and the Distr shared folder on this computer.
To create a new shared folder, run the command below:
New-SmbShare -Name Scripts -Path C:\PS -FullAccess woshub\mun_admins, woshub\mun-man01$ -ChangeAccess "woshub\mun-man01_scripts_rw" -ReadAccess "$env:USERDOMAIN\domain users" –description "PowerShell scripts for admin"
In this example, we created a shared folder and granted access to domain groups and one computer account.
Additionally, when creating a shared folder, you can use the following options:
-CachingMode [None|Manual|Programs|Documents|BranchCache]–set a caching mode for offline access (Windows offline files);-EncryptData $True– to enable SMB traffic encryption;-FolderEnumerationMode [AccessBased | Unrestricted]– to enable Access-based Enumeration. Allows to hide objects a user doesn’t have permission to access from the shared folder;-CompressData $True– to enable compression when sending files over SMB;-ConcurrentUserLimit 50– to set a limit of simultaneous connections to the folder (0 by default, unlimited);-Temporary– to create a temporary shared folder (disappears after the next Windows restart).
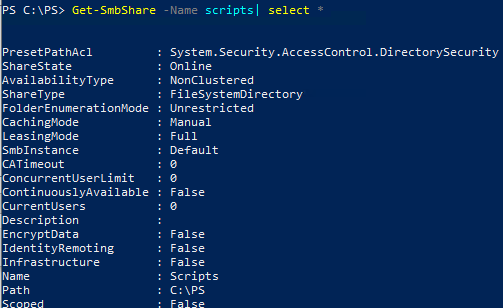
You can display a full list of shared folder settings:
Get-SmbShare -Name scripts| select *
To remove a network shared folder:
Remove-SmbShare Scripts
To add write permission for a user to the list ACL of the shared folder:
Grant-SmbShareAccess -Name Scripts -AccountName "woshub\b.hoffmann" -AccessRight Change –force
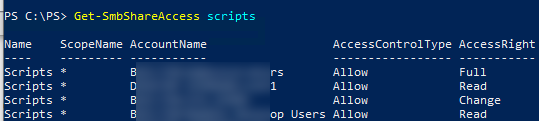
Display the current shared folder access list:
Get-SmbShareAccess scripts
To remove a security group from a share’s ACL:
Revoke-SmbShareAccess -Name Scripts -AccountName Everyone –Force
To force block access to a shared folder (a deny permission has a higher priority):
Block-SmbShareAccess -Name Scripts -AccountName woshub\ExternalGuests -Force
You can get the current NTFS ACL for a shared folder using this command:
(get-acl \\mun-man01\scripts).access
To change NTFS permissions, use the Set-Acl cmdlet (learn more about how to manage NTFS permissions using PowerShell).
How to View and Manage Open Files in Windows Shares?
You can use SMBShare cmdlets to view a list of files opened by users on a shared folder on a Windows file server.
To display a list of opened files with usernames, computer names (IP addresses), and file paths:
Get-SmbOpenFile|select ClientUserName,ClientComputerName,Path,SessionID
To show a list of files opened by a specific user:
Get-SMBOpenFile –ClientUserName "woshub\b.hoffmann" |select ClientComputerName,Path
To close a file a user opened and locked by a remote user:
$sessn = New-CIMSession –Computername munfs01
Get-SMBOpenFile -CIMSession $sessn | where {$_.Path –like "*sale_report2022.docx"} | Close-SMBOpenFile -CIMSession $sessn
Map SMB Network Drives with SmbMapping Cmdlets
SmbMapping cmdlets are used to manage network drives.
To map a network shared folder to the network drive U:, run the command below:
New-SmbMapping -LocalPath U: -RemotePath \\munfs01\scripts -UserName b.hoffmann -Password my22pass –Persistent $true -SaveCredential
- Without the Persistent option, the mapped network drive will only be available until the computer is restarted;
- The SaveCredential option allows saving user credentials to the Windows Credential Manager.
To display a list of mapped network folders:
Get-SmbMapping
To remove a network drive:
Remove-SmbMapping U: -force