In this article, we will show how to install software on user computers in an Active Directory domain using GPO.
The built-in Windows GPO features allow you to deploy programs that are only distributed as MSI or ZAP packages. Other types of apps you will have to install in alternative ways: using SCCM, via GPO logon scripts, copying program files to computers using GPO, running one-time scripts, etc.
Extracting an MSI Package from an EXE Installer
Let’s see how to install the MSI software package on users’ computers via Windows Group Policies on the example of the Microsoft Teams client.
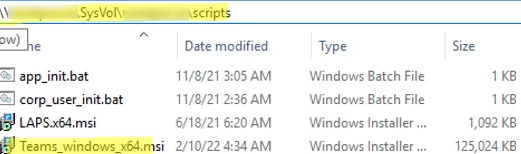
Download the MSI package with the Teams client (http://aka.ms/teams64bitmsi) and copy Teams_windows_x64.msi to the SYSVOL folder on the domain controller (\\woshub.com\SysVol\woshub.com\scripts).
Many apps are not provided in a form of MSI packages. Most often, developers distribute them as EXE files that are not suitable for deployment through GPO. However, in some cases, you can extract the MSI package from the EXE installation file:
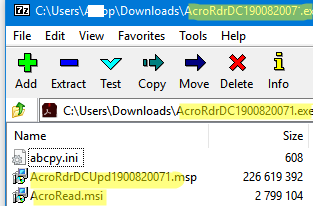
- Some EXE installers extract their files into the
%temp%directory during installation. So, then installing the program (just minimize the installation window), try to open this folder and find the installation MSI file in it. - Another way to get an MSI file is to try to open the setup EXE file using 7-Zip. Start 7-Zip and select File -> 7ZIP –> Open Archive. 7ZIP will try to open an EXE file as an archive. In our case, we got an MSI and MST files of Acrobat Reader from its EXE file. In our case, we successfully extracted the MSI and MST files from the Acrobat Reader installation EXE file.
Creating a GPO to Deploy Software to Domain Computers
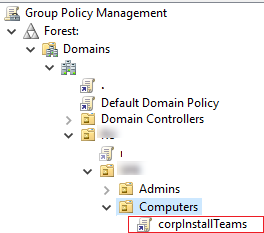
Then create a new domain Group Policy Object to install your software.
- Open the domain Group Policy Management console (
gpmc.msc); - Create a new policy (CorpInstallTeams) and link it to the OU with computers you want to install the app on (Create a GPO in this domain, and link it here);
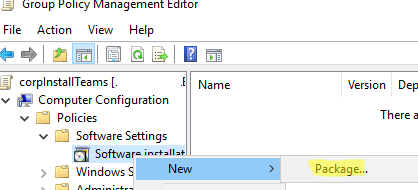
- Edit the GPO and go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Software Settings -> Software installation;
- Select New -> Package in the menu;
- Select your MSI file located in the SYSVOL directory (by the UNC path);
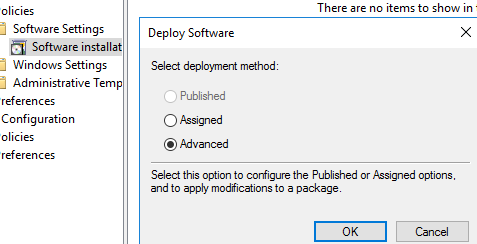
- Select Advanced and click OK;The Assigned option allows installing apps at the user logon. The Published option publishes apps to computers and users can install them in Add/Remove Programs.
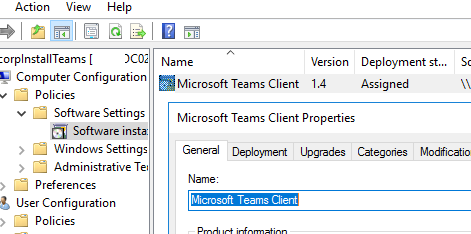
- In the next window, you can set additional MSI package options. I will only change the displayed name from Teams Machine-Wide Installer to Microsoft Teams Client;
- Click Advanced in the Deployment tab and check Ignore language when deploying this package;
- Restart your computer to update the GPO settings and the app will be installed the next time you boot your computer. It will appear in the list of installed Windows apps. You can find the installation events in the System section of the Event Viewer (filter the event list by the
Application Management Groupsource);Windows 11 has built-in Teams Chat, but it’s not a full-featured Microsoft Teams client. - You can display the detailed GPO processing status on the computer. To do it, enable the GPO option Display highly detailed status messages under Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> System. Now all background GPO processing tasks will be displayed when Windows starts. If any apps are installed using GPO, you will see the message: Installing managed software AppName.
How to Change MSI Package Options Before Deploying via GPO?
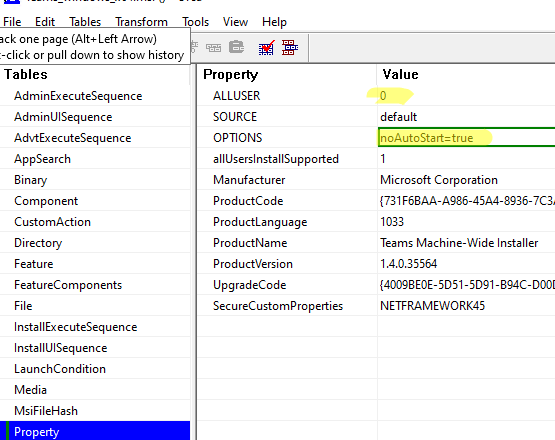
You cannot specify installation keys or parameters for MSI installation packages in the standard GPO interface. For example, when installing an anti-virus agent on a user’s computer, you must specify the IP address/FQDN of the management server. Or, when you install Teams from the command prompt using msiexec, you can disable the MS Teams client automatic startup and hide it from the list of installed apps (a local administrator won’t be able to remove the Teams client). To do it, the following command is used:
msiexec /i Teams_windows_x64.msi OPTIONS="noAutoStart=true" ALLUSERS=0
How to add setup options to an MSI package? To do it, MST transformation files are used. This file type allows you to change the default MSI package settings and use your installation scenario.
To create an MST file for an MSI package, you can use the ORCA tool (it is a part of Windows Installer SDK).
Open your MSI package using Orca.
Create a New Transformation and set your custom MSI package options in the Property section. I will change the following options for my Teams client:
- noAutoStart =
True - ALLUSERS =
0
Select Transform -> GenerateTransform and save the changes as MST file (teams_mod.mst). Copy the file to the SYSVOL directory.
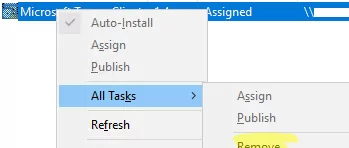
Then remove the previous rule to install the MSI package in the GPO (because you can add an MST file with package modifications only when creating an app installation rule).
Select All –> Task -> Remove.
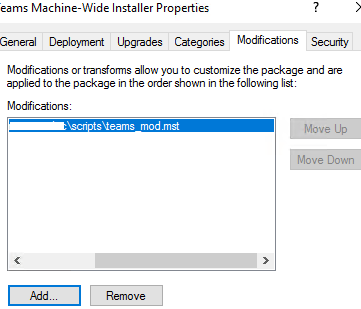
Create a new software deployment rule, select the MSI file from SYSVOL, and go to the Modification tab. Click Add. Select the MST file you created earlier.
The MST file will now be automatically applied during the MSI installation using the GPO and the application will be installed with the settings you need.
The main disadvantages of MSI installation through GPO:
- Only MSI and ZAP installers are supported;
- You cannot schedule app installation for the time you want. Simultaneous app installation on multiple computers (usually it occurs in the morning when computers are turned on) may result in high network and Domain Controllers load. In this case, it is better to use, SCCM with maintenance windows or WOL (Wake On LAN) settings;
- You cannot change the order in which the software is installed in the GPO. When you add a new installation package to GPO, it is installed last;
- You cannot get a report to know if the installation was successful or if there were any installation errors on the computers.