GPO logon scripts allow you to run a BAT or PowerShell script at computer startup or user logon/logoff. In some cases, an administrator wants a particular script (command/program) to be run for each user or computer only once and not run at the next logons.
To solve this task, you can use a standard logon script that checks for a certain flag on the computer. This can be a registry parameter, a text file on the disk, etc.
For example, you want a certain code block to be executed only once at the first user log on to a computer.
- Create the following BAT file (corp_user_init.bat) and save it to
%SystemRoot%\SYSVOL\sysvol\<domain name>\scriptson your domain controller:@echo off
IF EXIST C:\Users\%UserName%\AppData\app_init.txt GOTO END
date /t >> C:\Users\%UserName%\AppData\app_init.txt
time /t >> C:\Users\%UserName%\AppData\app_init.txt
REM Put your code here, which will be executed once
:ENDThe script creates a small text file in a user’s profile when it is run for the first time. When the script is run for the next time through the GPO, it checks if the file exists on a disk. If it does, the script has already been executed and the code doesn’t need to be run again. - Open the domain Group Policy Management console (
gpmc.msc); - Create a new policy and link it to an OU with users (or computers, but then you have to enable the Loopback Processing mode);
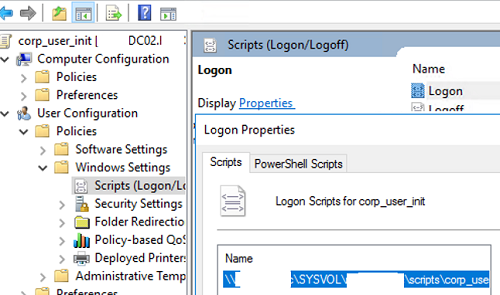
- Go to User Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Scripts (Logon / Logoff);
- Select Logon;
- Click Add and specify the path to your BAT file in SYSVOL (
\\woshub.com\SysVol\woshub.com\scripts);
- After updating Group Policy settings on a client computer, your script will be executed at user logon. Make sure that it has successfully created the app_init.txt file in a user’s profile.If the GPO with the script has not been applied, use the gpresult tool and troubleshooting methods described in the article Why GPO Is not Applied.
- At the next user logs on to a computer, the main script code will not be executed. So, the script is actually applied to the user only once.
Another way to run a script only once using GPO is to create a one-time task in the Task Scheduler.
- Save your script file (it may be either a BAT file or a PowerShell script) to the Sysvol folder on the domain controller (
\\<your_domain_name>\SysVol\<your_domain_name>\scripts); - Create a new GPO, link it to the user’s OU, and open its settings;
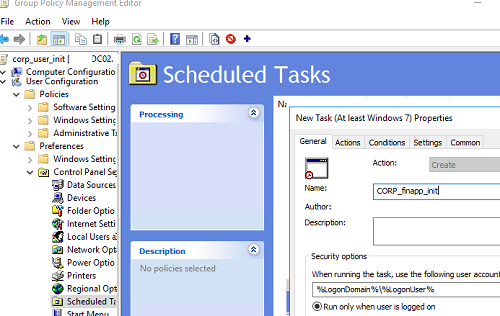
- Go to Preferences -> Control Panel Settings -> Scheduled Task -> New -> Immediate Task (At least Windows 7);
- Specify the task name;
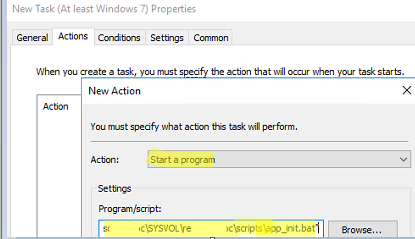
- Open the Actions tab, click New, and specify the full UNC path to your script file in SYSVOL;
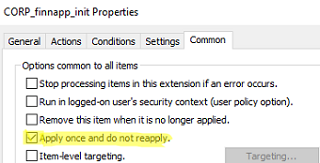
- Then go to the Common tab and check the Apply once and do not reapply option;
- This task will run on a computer only once at the first user logon.
If you want to run PowerShell scripts through a GPO, you need to configure the PowerShell script execution policy or use the
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass option when running your script (see an example here).