It can happen that you have forgotten your Windows login password and can no longer log on to your computer. This article shows you how to reset a forgotten password for the local administrator account using a Windows installation media (USB flash, DVD, or ISO image). This password reset guide covers both Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016.
You will need any Windows 10 or 11 installation media to reset the local administrator password. The easiest way is to create a bootable Windows USB flash drive using the Media Creation Tool or use the Rufus tool to write the downloaded Windows ISO image to a USB flash drive
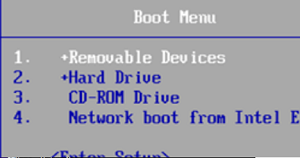
- When you start the computer, enter the BIOS/UEFI settings, and select your USB flash drive as the primary boot device. To do this, press
F1,F2orDel(depending on your hardware vendor), find the Boot Order/Boot Device Priority item (menu item names depend on the manufacturer and BIOS/UEFI firmware version), then set your Removable USB flash drive as the primary boot device; - When the computer starts, the message ‘Press any key to boot from CD/DVD/USB‘ should appear;
- The next thing you will see is the Windows Setup wizard. Use the key combination
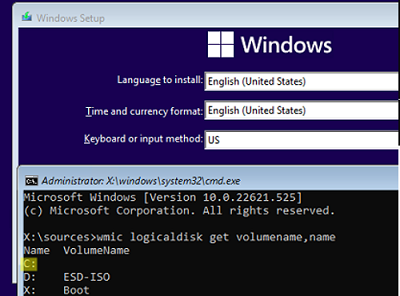
Shift+F10to open the command prompt; - The next thing you need to do is to find out the drive letter assigned to the partition where Windows is installed. Run the command:
wmic logicaldisk get volumename,name - You can see that in my example, Windows is on the
C:drive. This is the letter we will use in the following commands;
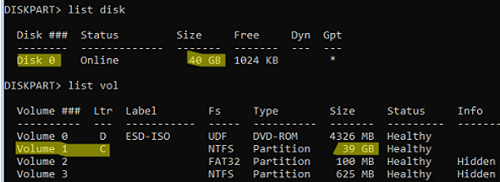
If your system partition is encrypted with Bitlocker and you have the password to decrypt it, you must first unlock the BitLocker-encrypted drive with the command:You can also identify partitions and their assigned drive letters in the WinPE environment using the diskpart command. For that, run the following commands one after the other:manage-bde -unlock C: -pw. Once you’ve done this, you can reset the administrator password.diskpart->list disk(to display a list of hard disks available) ->list vol(list partitions and their assigned drive letters). In this example, there is only one Disk 0 with a GPT partition table and three partitions: the EFI system partition (with the FAT32 file system, which contains the Windows EFI bootloader), the recovery partition (with the WinRE recovery environment), and the primary partition with the NTFS file system and size of 39GB (with the C drive letter assigned);
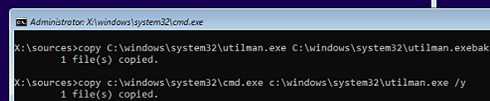
- Run the following command to back up the original utilman.exe file:
copy C:\windows\system32\utilman.exe C:\windows\system32\utilman.exebak - Then replace the utilman.exe file with the cmd.exe file:
copy c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe c:\windows\system32\utilman.exe /y
- Eject the bootable flash drive/Windows Setup ISO and restart the computer:
wpeutil reboot - Boot normally to Windows which is installed on your computer. On the sign-in screen, click on the Easy of Access (Accessibility) icon;
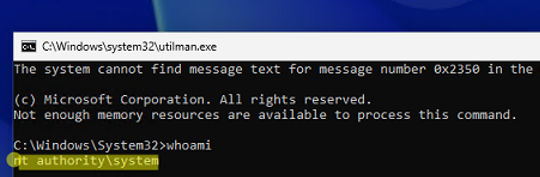
- A command prompt should appear. Make sure that the console is running under NT Authority\SYSTEM:
whoami
- You can manage local Windows accounts from this command line.
List the user accounts with administrator rights on the computer:
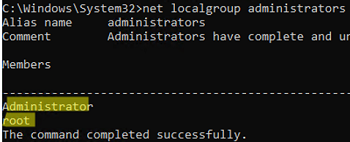
net localgroup administrators
There are two users in the Administrators group in this example. You can reset the password for any of these users to log on to Windows.
If the group is empty, this means that you need to assign administrator rights to one of the available local Windows users. List all local users:
net user
In order to add user1 to the local Administrators group, run the following command:
net localgroup administrators user1 /add
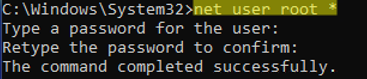
If you have no other users on the computer except the built-in Administrator account, you will need to reset the password for this account.If you use a Microsoft account on your computer, you can reset its password via https://account.live.com/password/reset. If you can’t recover your password in this way, you must enable your local Administrator account, reset its passwords, and sign in with it. You should then create a different local user with administrative privileges, or add a new user with a cloud-based Microsoft account. - To reset the user’s password (in this example, the username is root), run the command:
net user root *
Set a new password and confirm it (the new password must match your local Group Policy password settings);
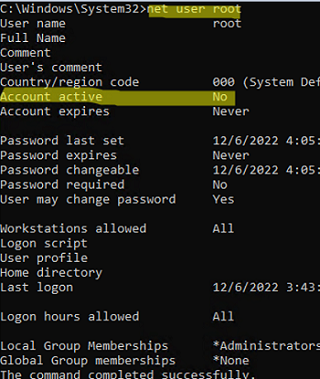
- Now you need to check if your account is enabled. Display the account information:
net user root
If the user is disabled (Account active: No ), enable it:
net user root /active:yes - Restart your computer and boot it again from the removable USB flash drive/ISO image. Replace the utilman.exe with the original file to avoid leaving a security hole in Windows:
copy c:\windows\system32\utilman.exebak c:\windows\system32\utilman.exe /y
After that, remove the flash drive and once again reboot the computer; - Now you can log on to Windows using the account that you reset the password for.In case you get an error ‘The Sign-in method you’re trying to use isn’t allowed’ when trying to sign in to Windows, it means that you have the corresponding group policy enabled on your computer. You can disable this policy option using the local GPO editor (gpedit.msc). You can also run this MMC snap-in from the command prompt on the Windows logon screen.
sethc.exe executable. If you have replaced sethc.exe with cmd.exe, just press the Shift key 5 times to open the command prompt on the Windows welcome screen (this triggers Sticky Keys mode and causes the sethc.exe executable to run).After resetting a user’s password, you will still have access to all files in the user’s profile, programs and settings, saved passwords in Windows Credential Manager, and all other data available for the user (note that you may lose access to EFS-encrypted files).
Note that if your computer is added to an Active Directory domain, it may be affected by various settings through domain Group Policies (GPOs). To help keep computers secure, Domain Administrators can assign specific policy settings to computers. For example, disable all local user accounts, remove local users from the Administrators group, or automatically change the password of the built-in admin account (via Windows LAPS). In that case, if you need to reset the administrator password on such a computer, you must first reset the local policies and clear the GPO cache, and then disconnect the computer from the network. You can then log in to Windows as a local administrator with the new password.