In this article we’ll look at how to configure RBL filters on Exchange 2016 and 2013. Let’s remember what RBL is. RBL (Realtime Blackhole List) is a service that stores the database containing a list of IP addresses of mail servers marked as spammers. RBL is the most often accessed over DNS protocol so these services are also called DNSBL (DNS Block Lists).
When receiving an e-mail from an unknown sender, the email server can automatically check these lists and block the e-mail from the IP addresses listed in the RBL service database. If the sender’s address matches with the value from one of the RBL lists, your Exchange server returns an SMTP error message 550 5.x.x as the response to the RCPT TO command, and the sender will receive a Non delivery report (NDR).
In Exchange 2013 and 2016, the Connection Filtering agent is responsible for blocking the connections based on the lists of IP addresses. The Connection Filtering agent includes:
- IP Block Lists – a black list of IP addresses from which the email must not be accepted (blocked senders);
- IP Allow Lists – a white list of IP addresses (allowed senders);
- RBL Providers – the list of RBL providers.
The first two lists are static and configured by the Exchange administrator manually. The list of RBL providers contains the list of third-party RBL services to be checked when receiving an e-mail message.
In Exchange 2013/2010, the anti-spam filtering could be enabled using the Install-AntispamAgents.ps1 script. Both filtering agents (Connection Filtering and Content Filtering) installed on the same server with Hub Transport role. In Exchange 2013, the transport role is divided into two components: Front End Transport and Back End Transport, and the anti-spam filtering feature is divided into two parts. The Front End server performs Connection Filtering and the Back End server does the Content Filtering (including the IMF filter – Exchange Intelligent Message Filter and the virus-detecting agent – Malware Agent).
In Exchange 2013, if the CAS and Mailbox roles are installed on the same server, the Install-AntispamAgents.ps1 script installs only the Content Filtering agent. It means that the RBL filtering won’t be available.
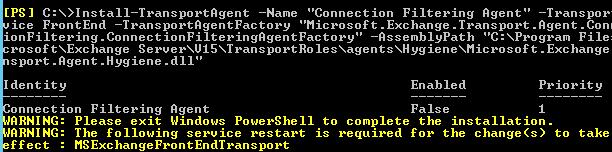
To install the Connection Filtering agent, use the Install-TransportAgent cmdlet:
Install-TransportAgent -Name "Connection Filtering Agent" -TransportService FrontEnd -TransportAgentFactory "Microsoft.Exchange.Transport.Agent.ConnectionFiltering.ConnectionFilteringAgentFactory" -AssemblyPath "C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\agents\Hygiene\Microsoft.Exchange.Transport.Agent.Hygiene.dll"
All roles (except for Edge Transport) are merged in Exchange 2016, so if you don’t have a dedicated server with the Edge Transport role, you will have to install antispam agents using the install-AntispamAgents.ps1 script on all servers. Then for the Exchange Transport service, you need to specify the addresses of internal SMTP servers, which should be ignored when checking for spam:
Set-TransportConfig -InternalSMTPServers @{Add="192.168.1.25","192.168.101.25"}
After the agent is installed, you need to enable it and restart the Front End Transport service:
Enable-TransportAgent -TransportService FrontEnd -Identity "Connection Filtering Agent"
Restart-Service MSExchangeFrontEndTransport
To make sure that the Connection Filtering agent is installed and running, do the following:
Get-TransportAgent -TransportService FrontEnd
Next you need to specify a list of RBL providers to be used.
Add-IPBlockListProvider -Name zen.spamhaus.org -LookupDomain zen.spamhaus.org -AnyMatch $true -Enabled $TrueTo change the text of the NDR message returned to the sender, execute this command:
Set-IPBlockListProvider zen.spamhaus.org -RejectionResponse "Your IP address is listed by Spamhaus Zen. You can delete it on page http://www.spamhaus.org/lookup/"You can add multiple RBL providers at once, having studied their peculiarities and commercial use policies.
You can display the list of currently used RBL as follows:
Get-IPBlockListProvider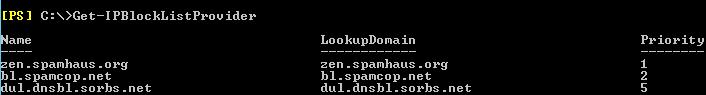
You can check if a certain IP address is in the RBL list with the following command:
Test-IPBlockListProvider -Identity zen.spamhaus.org -IPAddress x.x.x.x
By default the Connection Filter agent logs are saved to the folder
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\AgentLog.
You can get information about which of the RBL providers rejected the e-mail by performing a search on * .log files in this directory. To find the log file with the specified e-mail address, open the elevated cmd and run the commands:
Cd “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\AgentLog”
find /c "[email protected]" *.log | find ":" | find /v ": 0"
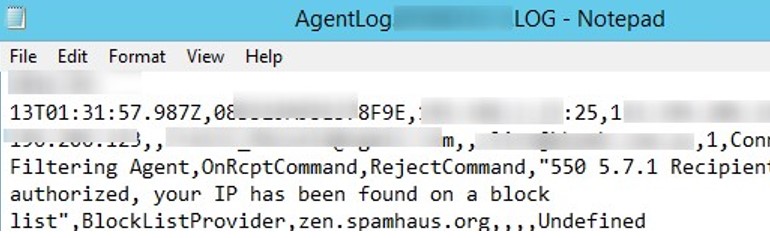
Then open the found *.log file in any text editor. Search for the rejected email address to detect the RBL provider that blocked the email and the blocking time.
This example shows that the email from [email protected] was rejected on your Exchange server by the RBL provider zen.spamhaus.org.
[email protected],,[email protected],1,Connection Filtering Agent,OnRcptCommand,RejectCommand,”550 5.7.1 Recipient not authorized, your IP has been found on a block list”,BlockLictProvider,zen.spamhaus.org,,,
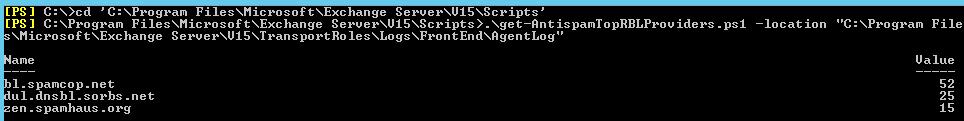
After the initial information is collected (it depends on the size of the SMTP traffic, and usually takes up to 2-3 days), the RBL filtering statistics can be displayed using the Get-AntispamTopRBLProviders.ps1 cmdlet:
.\get-AntispamTopRBLProviders.ps1 -location "C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\AgentLog"
The first time you start using RBL filtering, you need to carefully examine the filtering logs for false positives so as not to block emails from your partners. You can add such a trusted email addresses or domain names to the Exchange white list to bypass spam filtering:
Set-ContentFilterConfig -BypassedSenderDomains contoso1.com, contoso2.net,contoso3.co.uk
Or add the IP address of a specific SMTP server to the trusted ones:
IPAllowListEntry -IPAddress x.x.x.x
In addition, the following pre-installed PowerShell scripts can be used to obtain email filtering statistics by the Connection Filtering Agent:
- get-AntispamFilteringReport.ps1
- get-AntispamSCLHistogram.ps1
- get-AntispamTopBlockedSenderDomains.ps1
- get-AntispamTopBlockedSenderIPs.ps1
- get-AntispamTopBlockedSenders.ps1
- get-AntispamTopRBLProviders.ps1
- get-AntispamTopRecipients.ps1
To disable incoming email filtering, you need to disable the Connection Filtering Agent:
Disable-TransportAgent -TransportService FrontEnd -Identity “Connection Filtering Agent”
The RBL lists are quite effective to protect from unwanted email (spam), but in the most cases they have to be used in conjunction with other anti-spam methods to provide the robust anti-spam protection. In addition to RBL, you can manually block specific sender email addresses and domain in Exchange.

16 comments
Hey man, thanks so much for putting this up. I was feeling completely let down by all the features that MS dumped from Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2013. It’s good to see that there is a way to re-enable this crucial functionality. Thank you, again!
Fantastic job. Well done. Thank you.
Thanks for sharing the same. My Exchange 2013 is running on CU1, Build Number 15.0.620.29. Can I install Connection Filtering agent on this version of Exchange 2013 or it require Exchange Server 2013 Service Pack 1. please clarify
Hi,
I’ve followed above steps but it seems Connection filtering agent doesn’t pick up anything. When I run get-AntispamTopRBLProviders.ps1 it doesn’t show anything and there are no logs in AgentLog for connection filtering agent. I’m also running Exchange 2013 SP1 build 15.0.847.32 CAS/MBX.
Please help!
Do you install Connection Filtering Agent using this command:
Install-TransportAgent -Name “Connection Filtering Agent” -TransportService FrontEnd -TransportAgentFactory “Microsoft.Exchange.Transport.Agent.ConnectionFiltering.ConnectionFilteringAgentFactory” -AssemblyPath “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\agents\Hygiene\Microsoft.Exchange.Transport.Agent.Hygiene.dll”
or using $env:ExchangeInstallPath\Scripts\Install-AntiSpamAgents.ps1 ?
Check that the Connection Filtering agent is running:
Get-TransportAgent -TransportService FrontEnd
Hi,
At first I did. I’ve used exact same cmdlet to install Connection filter agent, enable agent and set IPBlockProviders list but it didn’t work. Next I have tried to install Connection filtering agent on backend and set up exact same way. Now I have positive results when running get-AntispamTopRBLProviders.ps1. To install Connection filter agent on backend I’ve used above cmdlet Install-TransportAgent but without “-TransportService FrontEnd”. It makes sence since I do not have Edge server, just CAS/MBX.
Worked like a charm. 5000 spam items rejected by SpamCop in the first 12 hours!
Thanks a lot for publishing this.
This was working great for me for several months in a test environment (2 CAS/Mailbox servers in a DAG, no Edge server), now it has stopped. Updates to log files in “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\AgentLog” have stopped being added. “Get-TransportAgent -TransportService FrontEnd” reports that the Connection Filtering Agent is Enabled. “Get-IPBlockListProvider” shows the three RBLs I had configured, so no change there.
I am running a DAG and tried flipping which server receives direct messages from the Internet, but the second server suffers the same problem (ran same install scripts and validation checks — both servers report that it’s set to Enabled).
Any ideas? The only thing I can think that might have changed is that the trial period for Exchange in the test environment expired. However, I’ve not seen anything that indicates spam or connection filtering stops when the trial period ends (everything else appears to still work). This is an ongoing test bed for us for trialing stuff before moving to our production Exchange servers, so we need to solve this. I know running Connection Filtering on the FrontEnd is not officially supported, so I hope someone here can offer some suggestions.
If I need RBL only and have CAS/MBX roles on diferent servers, do I need do it on CAS server only? Without any additional steps on MBX server?
Thanks.
Use netstat -ano | findstr /C:”:25 ” to find the PID of the process that listens on port 25
Then use the PID to find the service name using: tasklist /SVC /FI “PID eq xxxx” Use the PID id from step 1
C:\>netstat -ano | findstr /C:”:25 ”
TCP 0.0.0.0:25 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 21804
TCP [::]:25 [::]:0 LISTENING 21804
C:\>tasklist /SVC /FI “PID eq 21804”
Image Name PID Services
========================= ======== ============================================
MSExchangeFrontendTranspo 21804 MSExchangeFrontEndTransport
In this case you need the “-TransportService FrontEnd” parameter.
Cool that it is possible to view how many Blocks there have been made, but is it also possibe to view what domain and or IP addresses it is there were blocked?
For such a report, you can combine data from several scripts, such as
get-AntispamFilteringReport.ps1
get-AntispamSCLHistogram.ps1
get-AntispamTopBlockedSenderDomains.ps1
get-AntispamTopBlockedSenderIPs.ps1
get-AntispamTopBlockedSenders.ps1
get-AntispamTopRBLProviders.ps1
get-AntispamTopRecipients.ps1
Hello,
I recomend use this RBL:
dnsbl.spfbl.net
Thank you for the tutorial is exactly what I needed.
I am on exchange 2013 CU16
after I installed and configured this I can’t seem find the location
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\AgentLog
I have only this location
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd on the folder I have two folders Connectivity and protocollog.
Thank you
I wanna know how many emails has been blocked .
Theres a step missing.
The folder needs to be manually created:
mkdir “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\Logs\FrontEnd\AgentLog”
The IPAllowListEntry -IPAddress x.x.x.x cmdlet does not seem to be working. I do not get an error but i dont get anything either
I did not find this cmdlet but i did find the:
ADD-IPAllowListEntry -IPAddress x.x.x.x
This cmdlet seems to work and provide output, And the output is the same as the:
GET- IPAllowListEntry.