You can use the Group Policy to create and deploy scheduled tasks to domain computers. For example, you can create a task that automatically logs out users or shuts down computers at a specified time, runs a script, etc.
In this example, we will create a new Scheduler task that displays a pop-up notification and distribute it to users’ computers using Group Policy Preferences.
- Open the Group Policy Management console (
gpmc.msc), create a new GPO, and link it to an Organizational Unit with users or computers you want to assign the task to (if you assign the GPO to an OU with computers, enable the Configure user Group Policy Loopback Processing mode under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Group Policy, see the guide here);
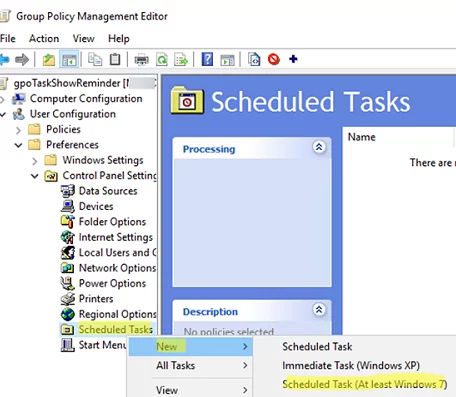
- Go to User Configuration -> Preferences -> Control Panel Settings -> Scheduled Tasks;
- Create a new scheduled task: New -> Scheduled task (At least Windows 7);The Immediate Task (at least Windows 7) item allows to create of a task that will run only once, but as quickly as possible (immediately after the next Group Policy update on the client).
- You will see a form similar to the standard Windows Scheduler task configuration window. Configure the settings of your task;
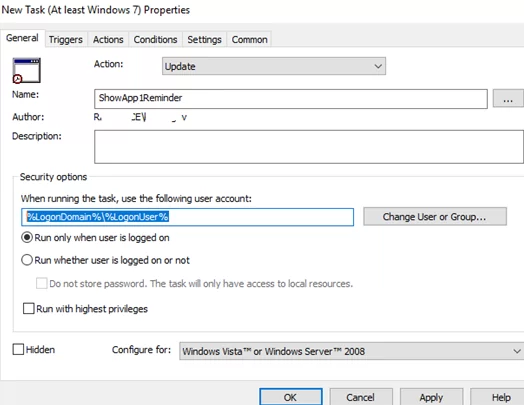
- On the General tab, set Action =
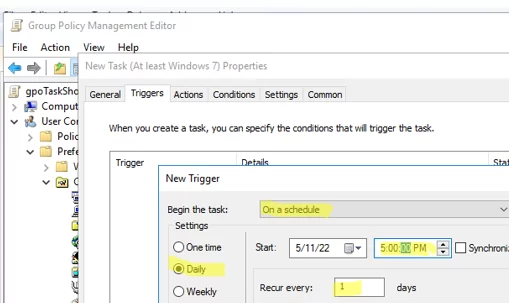
Update, enter the task name. To make the task run on behalf of the current user, enter%LogonDomain%\%LogonUser%here. To run the task as administrator, check the Run with highest privileges option;If you create a task in the Computer Configuration GPO section, you may run the job on behalf of the system (NT AUTHORITY\System). - Navigate to the Triggers tab. Specify the date and time when you want to run the task. In my case, it is 5 PM every day. Select New -> Begin the task On a schedule -> Daily, and specify the time to start the task;
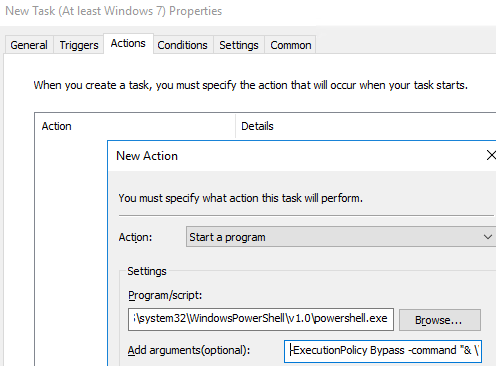
- On the Actions tab, specify a command or a script you want to run using the Task Scheduler. Configure the following task options:
Action: Start a program
Program/Script:C:\WINDOWS\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Add Arguments (optional):-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -command "& \\woshub.com\SysVol\woshub.com\scripts\ShowReminder.ps1"You copy the file of your PS1 script to user computers using GPO or run it directly from the UNC path. In my example, I am running a PowerShell script that displays a pop-up notification from the SYSVOL directory on the domain controller. To bypass PowerShell script Execution Policy, I use the-ExecutionPolicy Bypassoption. - Restart a user’s computer to apply the GPO. Open the Task Scheduler (
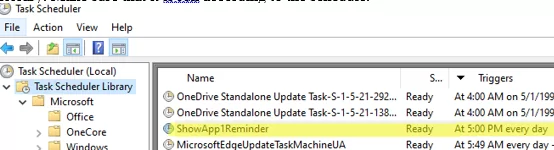
taskschd.msc) and make sure that a new task has appeared in the Task Scheduler Library. Make sure that it is run according to the schedule.
Start-ScheduledTask YourTaskName1Note that unlike GPO logon scripts you may configure it to be run only when a computer is started/shutdown or when a user logon/logout, scheduled tasks can be run at any time or after a specific trigger event occurs. See an example of how to run a script (do an action) when starting (exiting from) an app in Windows.
1 comment
I have created a FailedLogon task in GPO. The task gets deployed if I run it as SYSTEM. But when trying to run it under a service account srv_tasks it doesn’t schedule the task. And in the event logs I see this:
The computer ‘FailedLogonTask’ preference item in the ‘FailedLogonTask’ Group Policy Object did not apply because it failed with error code ‘0x80070005 Access is denied.’ This error was suppressed