Windows Server Core is a good platform to host the Active Directory domain controller role due to fewer resource requirements, increased stability and security (due to less code and updates). In this article, we’ll show how to install a domain controller on Windows Server Core 2019 in a new or existing Active Directory forest using PowerShell.
How to Install Active Directory Domain Controller Using PowerShell?
Install the Windows Server Core on a new host (physical or virtual), configure the basic host settings: set its hostname, network settings (static IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS), date/time, time zone, etc.
Rename-Computer -NewName hb-dc03
Get-NetAdapter
$ip = "192.168.13.11"
$gw="192.168.13.1"
$dns = "192.168.13.10"
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias Ethernet -IPAddress $ip -AddressFamily IPv4 -PrefixLength 24 –DefaultGateway $gw
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias Ethernet -ServerAddresses $dns
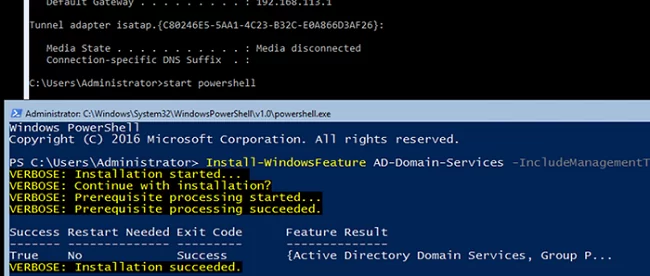
The next step is to install the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) role. To do it, run the following command in the PowerShell console:
Install-WindowsFeature AD-Domain-Services –IncludeManagementTools -Verbose
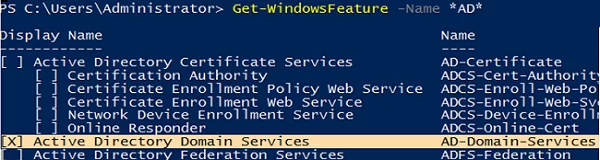
Get-WindowsFeature -Name *AD*
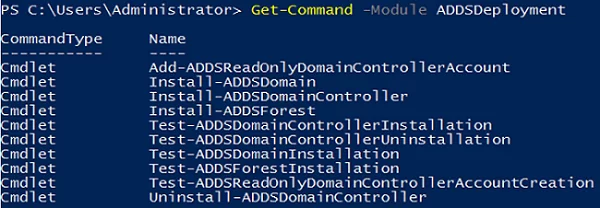
After installing the ADDS role, you can use ADDSDeployment module cmdlets to deploy a new domain, forest, or additional domain controller:
Get-Command -Module ADDSDeployment
There are three possible scenarios:
- Installation of new Active Directory forest:
Install-ADDSForest -DomainName woshub.com -ForestMode Win2016 -DomainMode Win2016 -DomainNetbiosName WOSHUB -InstallDns:$true - The
Install-ADDSDomaincmdlet allows to create a new domain in an existing Active Directory forest Install-ADDSDomainController– allows to add a new (additional) domain controller to an existing Active Directory domain
Add-ADDSReadOnlyDomainControllerAccount cmdlet.In most cases, you will use the 3rd scenario — adding an additional domain controller to an existing Active Directory domain.
Dcdiag /v and check the AD replication (repadmin /showrepl and repadmin /replsum). Make sure that you have an up-to-date AD domain controller backup.In the simple scenario, when you want to add a new extra DC to the Default-First-Site-Name site, run this command:
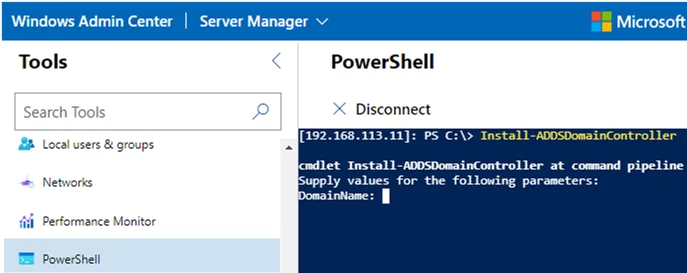
Install-ADDSDomainController -DomainName woshub.com -InstallDns -Credential (get-credential WOSHUB\Administrator) -DatabasePath "D:\ADDS\DB" -LogPath "D:\ADDS\Log" -SysvolPath "D:\ADDS\SYSVOL"
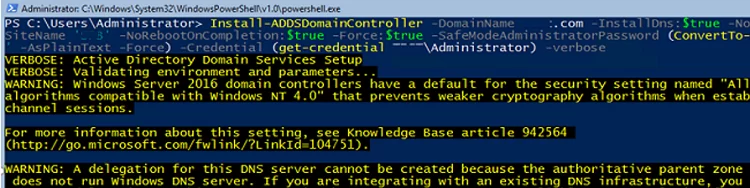
%SYSTEMROOT%\NTDS and %SYSTEMROOT%\SYSVOL.Also, you can specify the Active Directory site you want to place your new domain controller. We will also specify that the DC will be the Global Catalog and set the DSRM (Directory Services Restore Mode) password using the ConvertTo-SecureString command:
Install-ADDSDomainController -DomainName woshub.com -InstallDns:$true -NoGlobalCatalog:$false -SiteName 'Hamburg' -NoRebootOnCompletion:$true -Force:$true -SafeModeAdministratorPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString 'R0DCP@ssw0rd' -AsPlainText -Force) -Credential (get-credential WOSHUB\Administrator) –verbose
Check the command output carefully, if it is ok, then restart your host:
Restart-Computer
Checking Domain Controller Health on Server Core
After the domain controller installation, do some basic checks to make sure that the new domain controller has been successfully added to the domain and takes part in replication.
You can manage a domain controller on Windows Server Core from another server using the standard graphic Active Directory snap-ins (dsa.msc, gpmc.msc, dnsmgmt.msc, dssite.msc, adsiedit.msc, domain.msc) or from a computer running Windows 10 with RSAT installed (Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tool).
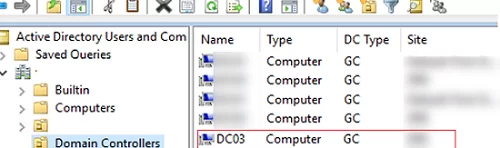
Open the ADUC (dsa.msc) console on any computer and make sure that the new DC appeared in the Domain Controllers OU.
After Windows Server Core restart, you must login to the host under a domain administrator account.
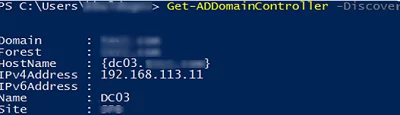
Using the Get-ADDomainController cmdlet, make sure that the domain controller is located on the correct AD site:
Get-ADDomainController -Discover
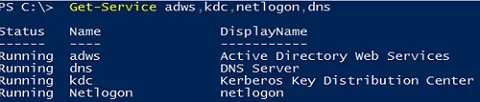
Check that Active Directory services are running:
Get-Service adws,kdc,netlogon,dns
In addition to the built-in hidden admin shares, the SYSVOL and NETLOGON folders must be shared:
Get-SMBShare
Make sure that there are ADDS events in the Event Viewer:
Get-Eventlog "Directory Service" | Select-Object entrytype, source, eventid, message
Get-Eventlog "Active Directory Web Services" | Select-Object entrytype, source, eventid, message
Then perform a test using the dcdiag command (all stages must be Passed), and check replication between the DCs using the following commands:
repadmin /replsummary
or
Get-ADReplicationFailure -Target DC03
Check where the FSMO roles are located in your domain and forest. If necessary, transfer the FSMO roles to your new DC:
Netdom /query FSMO
Installing an AD Domain Controller Using Windows Admin Center (WAC)
To install a domain controller in Windows Server Core, you can also use Windows Admin Center (WAC) web interface.
- Add your Windows Server Core host to the Windows Admin Center interface;
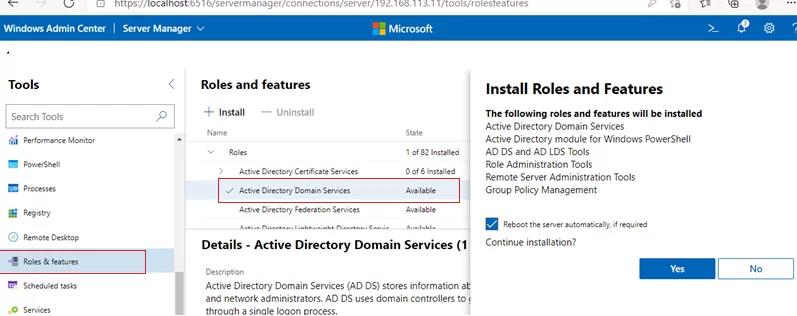
- To install the ADDS role, open the Roles and Features section, select Active Directory Domain Services in the list of available roles and click Install;
- Confirm the installation of the role and administration tools;
- To promote the Windows Server Core to the domain controller, open the PowerShell web console and use the cmdlets shown above to configure the DC;
- When the DC installation is over, restart Server Core and reconnect it to WAC using a domain account;
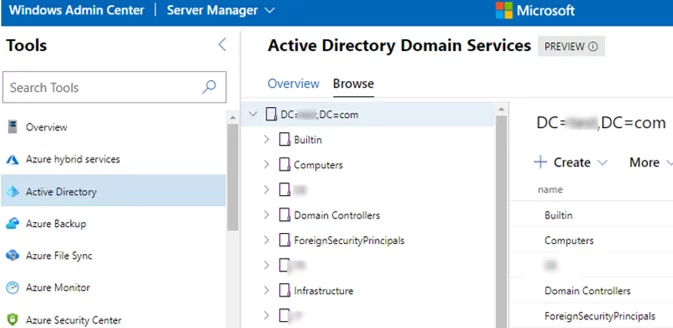
- To manage Active Directory from the web interface, install a special WAC extension (it is available in Preview mode yet). So a new section will appear in your Windows Admin Center, where you can view and manage your AD tree.