In this quick note, I’ll show you how to run multiple cmd or PowerShell commands in one line. Sometimes you have to do this when you invoke PowerShell commands from external programs, Windows Task Scheduler, logon scripts, when you need to bypass PowerShell Execution Policy, or when you have to quickly pass a piece of code to a user to diagnose/troubleshoot issues on their computer.
Executing Multiple Commands in One Line in Windows CMD
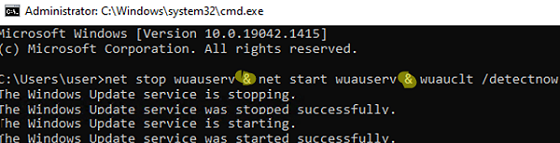
You can use the & cmd operator to run several commands one after another in one line. For example:
net stop wuauserv & net start wuauserv & wuauclt /detectnow
If you want the second command to be executed only if the previous one was successful, use the && format:
ipconfig /flushdns && ipconfig /renew
You can use a reverse condition: the second command will be executed only if the first one returned an error:
net stop wuauserv6 || net start wuauserv
Run Multiple PowerShell Commands in One Line
If you use an ampersand symbol to separate commands in one line, the following error appears:
The ampersand (&) character is not allowed. The & operator is reserved for future use.
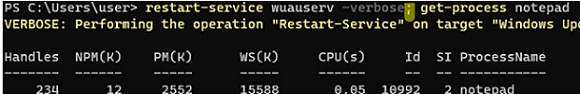
Instead of &, a semicolon ( ; ) is used in PowerShell to separate commands in one line:
restart-service wuauserv -verbose; get-process notepad
This one-liner PowerShell command will restart the Windows service and after the first command completes, it will list the information about the Windows process.
A popular example of a command abbreviation in PowerShell is a pipe, which allows you to pass the result of one command to the next one using a pipeline. In PowerShell, the “|” symbol is used as a pipeline operator. Here is an example of a pipeline command:
Get-Service -Name wususerv | Stop-Service
The same code can be written entirely in several lines:
$service = Get-Service -Name wususerv
$serviceName = $service.Name
Stop-Service -Name $serviceName
The pipeline allows to reduce the code size, and the code became more simple and readable.
To run multiple PowerShell commands using Start -> Run menu, use the format below:
powershell -command &"{ipconfig /all; ping woshub.com; pause "Press any key to continue"}"
If you run the same commands via the PowerShell console, use the following syntax:
powershell -command {ipconfig /all; ping woshub.com; pause "Press any key to continue"}
When running multiple PowerShell commands through the Windows Task Scheduler, you can use this format:
c:\windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -Command {Get-EventLog -LogName security; ipconfig /all ; get-service servicename}"
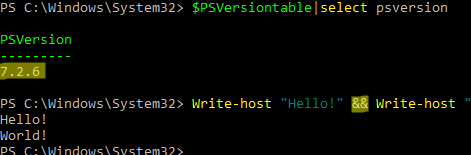
New && and || operators are available in modern PowerShell Core version 7.x. They work the same as in cmd.
$PSVersiontable.The && operator runs PowerShell commands to the right of it if the command on the left has been successful:
Write-host "Hello!" && Write-host "World!"
The || operator is used when you want to run a command if the previous command returned an error:
get-service servicename || write-host "missing service"