If you are using mapped network drives, you probably noticed that they are not showing in the apps running with administrator privileges (including cmd and PowerShell). The default User Account Control (UAC) settings don’t allow to access mapped network drives (via net use) from applications running in elevated mode (Run as administrator). This means that when you run the command prompt or a file manager (like Total Commander) with elevated privileges, they won’t display the drive letters of the mounted shared folders.
You may face such a problem if the following conditions are true:
- Network drives are mapped in the user’s session (via GPO or manually via
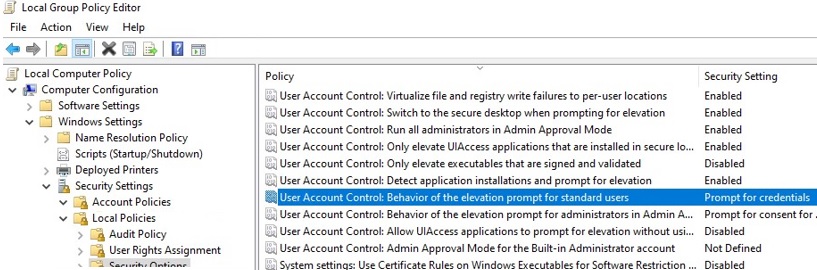
net use); - UAC is enabled on the computer (the GPO parameter User Account Control: Behavior of the elevation prompt for administrators in Admin Approval Mode is set to default value “Prompt for credentials”);
- The current user has local administrator permissions on the computer and runs the app in the “Run as administrator” mode.
In this case, network drives are displayed in Windows File Explorer and in apps, but are not displayed in any applications running in elevated mode.
In this article we’ll show how to allow access to mapped network drives from the apps running in the elevated mode on Windows 10. This problem occurs both for network drives mapped through Group Policy and for the folders connected by users.
Mapped Network Drives are not Showing in Windows Apps
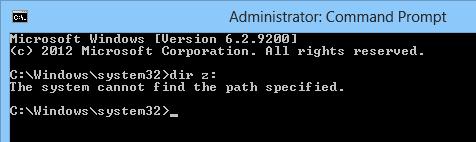
Let’s check that you cannot access the mapped network drive connected in normal mode from an elevated application with UAC enabled. For example, let’s open a command prompt with user permissions and check if you can access the contents of the mapped network drive Z:\.
Net use
Dir z:
The command should list the contents of the shared network folder.
If you open the command prompt in the current session as administrator, and try to access the same drive – you’ll receive the message that the path to the drive has not been found:
The system cannot find the path specified.
This behavior of Windows can cause some inconvenience when you frequently run applications in elevated mode. It is possible to run applications without administrator privileges, but this is not always applicable.
Why does it happen? This peculiarity is related to UAC mechanism for a user with the local administrator privileges. The matter is that when this user log in, two access tokens are created: the first token provides access with disabled administrator privileges (the filtered access token, with which most of the apps are running) and the second is the administrator token with full privileges in the system (all apps approved for elevation by UAC are running in this context).
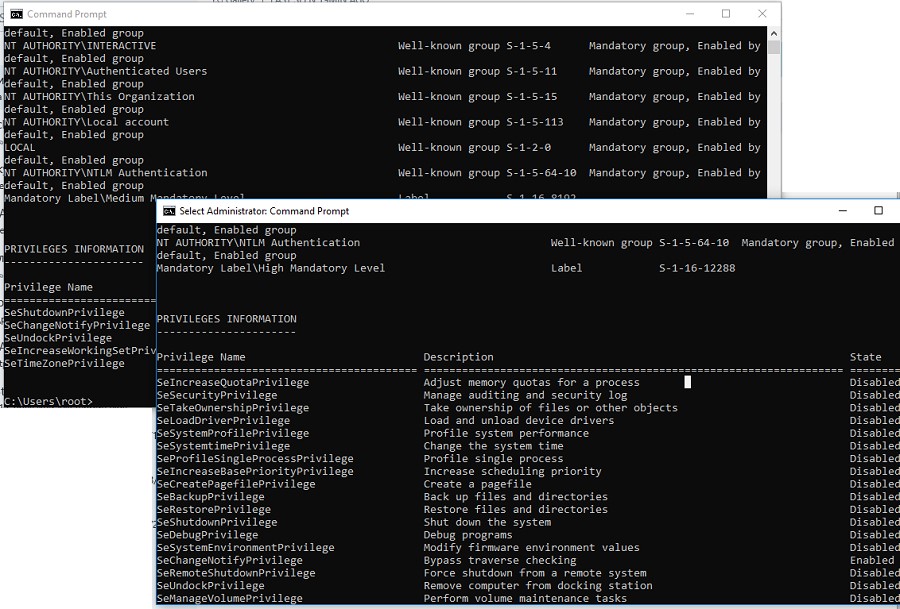
You can use whoami /all command in two cmd.exe sessions (normal and elevated) of the same user and compare the current privileges, you can see that they are very different. The following table lists the differences in the security groups and current privileges in each session.
| Normal user session | Elevated user session | |
| Security group | Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory Level Label S-1-16-8192 | Mandatory Label\High Mandatory Level Label S-1-16-12288 |
| Privileges | SeLockMemoryPrivilege SeMachineAccountPrivilege SeShutdownPrivilege SeChangeNotifyPrivilege SeUndockPrivilege SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege SeTimeZonePrivilege | SeLockMemoryPrivilege SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege SeMachineAccountPrivilege SeSecurityPrivilege SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege SeLoadDriverPrivilege SeSystemProfilePrivilege SeSystemtimePrivilege SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege SeCreatePagefilePrivilege SeBackupPrivilege SeRestorePrivilege SeShutdownPrivilege SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege SeChangeNotifyPrivilege SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege SeUndockPrivilege SeManageVolumePrivilege SeImpersonatePrivilege SeCreateGlobalPrivilege SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege SeTimeZonePrivilege SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege SeDelegateSessionUserImpersonatePrivilege |
Applications under the same user may be run in two contexts when UAC enabled (privileged and unprivileged). When you map shared network folders, the system creates symbolic links (DosDevices) that store the drive letter mapping to the UNC paths. These links are associated with the current process access token and are not available to other tokens.
The reverse problem may also occur: when the user with administrator permissions on the computer is connecting network drives using the Group Policy logon scripts, scheduled tasks or SCCM jobs (which are running with elevated privileges), these drives are not visible to the user in File Explorer (unprivileged process).
As a workaround, you can mount network drives from the elevated command prompt using the commands: net use or rundll32 SHELL32.dll,SHHelpShortcuts_RunDLL Connect .
Enablelinkedconnections: Enabling Mapped Drives in the Elevated Apps
There is an easier solution. To implement it, you have to make some changes to the registry:
- Open the registry editor (regedit.exe);
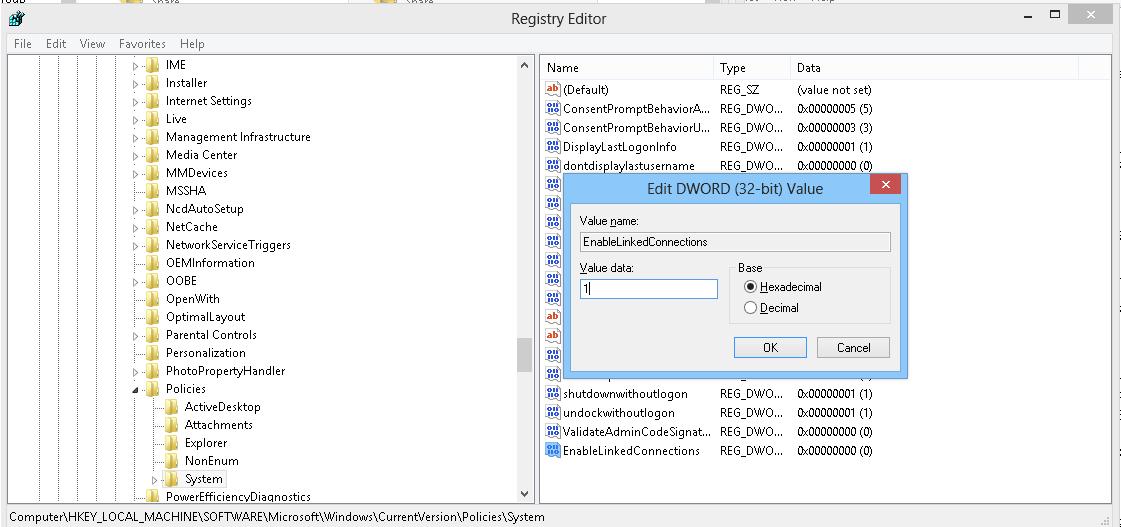
- Go to the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System;
- Create a new parameter (DWORD type) with the name EnableLinkedConnections and the value 1 ;Tip. The same change can be done with a single command:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" /v "EnableLinkedConnections" /t REG_DWORD /d 0x00000001 /for with PowerShell:
New-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System' -Name EnableLinkedConnections -Value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' - Restart your computer (or restart the LanmanWorkstation service with the command:
get-service LanmanWorkstation |Restart-Service –Force, and re-logon Windows).
After restarting the computer, make sure that the user can see the mapped network drives in programs running with admin rights. The reverse statement is true: all network drives mapped in the elevated mode will also be available in the unprivileged user session.
This works on all Windows versions starting from Vista to Windows 10/Windows Server 2019.
How it works? After you enabled the EnableLinkedConnections registry parameter, LanmanWorkstation and LSA (lsass.exe) will check for a second access token associated to the session of the current user. If this token is found, the list of the mapped network drives will be copied from one token to another. Thus, the network drives mapped in the privileged mode will be visible in the normal mode, and vice versa.
mklink /D c:\docs \\dublin-fs1\docs
You can access this drive in both normal and elevated mode. It should be noted that one of the drawbacks of this method is that you access the shared folder as a current user. It is impossible to use the account of another user as in the case of net use command.
After enabling the EnableLinkedConnections parameter, mapped drives will also become available from the Scheduled Tasks launched under the current user. If the task is run as LocalSystem or another user, the mapped network drives of the current user will be unavailable.


4 comments
Great! Well explained!
I remember having a hard work to understand why my mapped drives were not appearing in the elevated prompts… Until I found a technet post that saved my life lol
I faced this issue before and had to change the registry parameter to solve it.
Now is more clear and understood.
Many thanks!
did not work for Quickbooks Desktop Enterprise
This did not work for me. Environment: VirutalMachine: Guest: Win 10 Pro, Host: Win 10 Pro, Mapped Network Drives: “\\vmware-host\Shared Folders\*”.
I found that by creating a batch file that causes and elevated “Administrator: Command Prompt” and a All users Startup (shell:common startup”) I am able to automate the mapping. Note that the normal File Manager mapping works.
The code to get an elevated command prompt can be found at: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11525056/how-to-create-a-batch-file-to-run-cmd-as-administrator