OpenVPN is an open-source software suite that is really one of the most popular and easiest solutions for implementing a secure VPN. OpenVPN allows you to combine a server and clients (even those behind a NAT or firewall) into a single network, or to connect networks of remote offices. You can deploy a server part of OpenVPN almost in all available operating systems, including Linux, Windows, MacOS, and *BSD. You can install an OpenVPN server on Windows Server 2022/20119/2016/2012R2 or even on a computer running desktop Windows edition (Windows 10 or 11).
In this article, we will show how to install and configure an OpenVPN server on a computer running Windows 10, set up an OpenVPN client on another Windows device, and establish a secure VPN connection.
How to Install OpenVPN Server Service on Windows?
Download the OpenVPN MSI installer for your Windows version from the official website (https://openvpn.net/community-downloads/). In our case, this is OpenVPN-2.5.7-I602-amd64.msi (https://swupdate.openvpn.org/community/releases/OpenVPN-2.5.7-I602-amd64.msi).
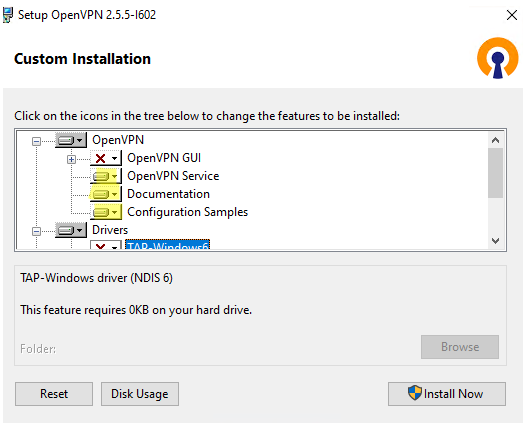
Run the setup and select OpenVPN Service to install. If you want your OpenVPN server to start automatically, you may not install OpenVPN GUI.
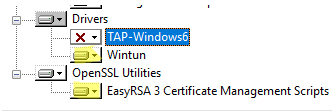
OpenVPN 2.5 (and newer) supports the WinTun driver from the WireGuard developers. This driver is faster that the default TAP OpenVPN driver. We recommend installing Wintun driver instead of TAP-Windows6.
Install the EasyRSA Certificate Management Scripts OpenSSL utility.
Complete the installation.
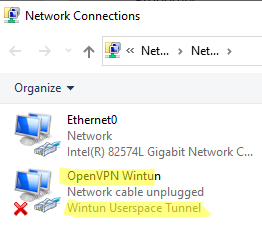
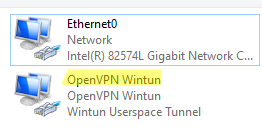
When the installation is complete, you will see a new network adapter Wintun Userspace Tunnel. This adapter is disabled if the OpenVPN service is not running.
Create OpenVPN Encryption Keys and Certificates
OpenVPN is based on OpenSSL encryption. This means that RSA3 keys and certificates must be used to establish a network connection between the client and the VPN server.
Open the command prompt and go to easy-rsa directory:
cd "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa"
Create a copy of the file:
copy vars.example vars
Open the vars file in any text editor. Check the paths to the OpenVPN and EaseRSA working folders.
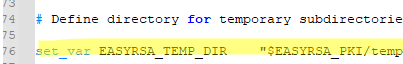
Be sure to edit the EASYRSA_TEMP_DIR variable as shown below:
set_var EASYRSA_TEMP_DIR "$EASYRSA_PKI/temp"
You may fill in the certificate fields (optional):
set_var EASYRSA_REQ_COUNTRY "DE" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_PROVINCE "BY" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_CITY "MUN" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_ORG "WOSHUB-Com" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_EMAIL "[email protected]" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_OU "IT dept"
Set certificate expiration dates:
set_var EASYRSA_CA_EXPIRE 3650 set_var EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE 825
Save the file and run the command:
EasyRSA-Start.bat
All of the following commands must be run in the EasyRSA shell:
Initialize PKI:
./easyrsa init-pki
You should see this message:
init-pki complete; you may now create a CA or requests. Your newly created PKI dir is: C:/Program Files/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/pki
Then generate the root CA:
./easyrsa build-ca
Enter a CA password twice:
CA creation is complete and you may now import and sign cert requests.
The command above has created:
- A root certificate of the Certification Authority:
C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\ca.crt - A Certification Authority key: C
:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\ca.key
Then generate a certificate request and a key for your OpenVPN server:
./easyrsa gen-req server nopass
The tool will generate two files:
req: C:/Program Files/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/pki/reqs/server.req
key: C:/Program Files/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/pki/private/server.key
Sign the request to issue a server certificate using your CA:
./easyrsa sign-req server server
Confirm the data by typing yes.
Then enter the CA password for your root CA.
The server.crt file will appear in the issued folder (C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\issued\server.crt).
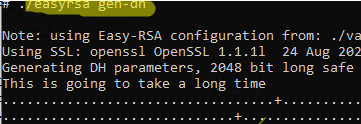
Then you can generate Diffie-Hellman keys (takes a long time):
./easyrsa gen-dh
To provide additional protection for your VPN server, it is recommended to enable tls-auth. This feature allows using HMAC signatures in SSL/TLS handshake, thus initiating an extra integrity check. Packets without such a signature will be dropped by the VPN server. This will protect you against VPN server port scanning, DoS attacks, SSL/TLS buffer overflows, etc.
Generate a tls-auth key:
cd C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\bin
openvpn --genkey secret ta.key
The C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\bin\ta.key file will appear. Move it to C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki folder.
Then you can generate keys for your OpenVPN clients. Each client connecting to your VPN server must have its own key pair.
There are several ways to generate OpenVPN keys and distribute them to clients.
In the example below, we will create a client key on the server and protect it with a password (PEM pass phrase):
./easyrsa gen-req testuser1
./easyrsa sign-req client testuser1
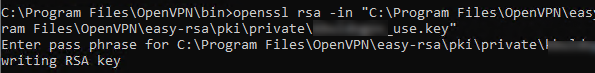
Copy the key file (C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\testuser1.key) to the client computer tell the user the password (voice, email, SMS). The client can disable the password protection for the key:
openssl rsa -in "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\testuser1.key"-out "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa\pki\private\testuser1_use.key"
If you want to generate a key that is not password protected, you need to run the command:
./easyrsa gen-req testuser2 nopass
You may create any number of keys and certificates for users on your VPN server. Generate keys and certificates for other clients in the same way.
You can revoke compromised client certificates:
cd C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa
EasyRSA-Start.bat
./easyrsa revoke testuser2
Therefore, we have generated a set of keys and certificates for the OpenVPN server. Now you can configure and run your VPN service.
OpenVPN Server Configuration File for Windows
Copy the configuration file template for the OpenVPN server:
copy "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\sample-config\server.ovpn" "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config-auto\server.ovpn"
Open server.ovpn in any text editor and make your settings. I am using the following OpenVPN configuration:
# Specify a port, a protocol and a device type port 1194 proto udp dev tun # Specify paths to server certificates ca "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\ca.crt" cert "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\issued\\server.crt" key "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\private\\server.key" dh "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\dh.pem" # Specify the settings of the IP network your VPN clients will get their IP addresses from server 10.24.1.0 255.255.255.0 # If you want to allow your clients to connect using the same key, enable the duplicate-cn option (not recommended) # duplicate-cn # TLS protection tls-auth "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\easy-rsa\\pki\\ta.key" 0 cipher AES-256-GCM # Other options keepalive 20 60 persist-key persist-tun status "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\log\\status.log" log "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\log\\openvpn.log" verb 3 mute 20 windows-driver wintun
Save the file.
Remember to open ports in the firewall for the OpenVPN port number you have specified on the client and on the server. You can open the port in Windows Defender using PowerShell.
Firewal rule for the OpenVPN server:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "AllowOpenVPN-In" -Direction Inbound -Protocol UDP –LocalPort 1194 -Action Allow
The rule for the client:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "AllowOpenVPN-Out" -Direction Outbound -Protocol UDP –LocalPort 1194 -Action Allow
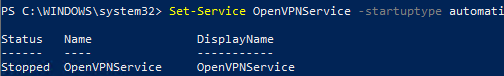
Then run the OpenVPN service and change its startup type to automatic. Use the PowerShell commands to enable the service:
Set-Service OpenVPNService –startuptype automatic –passthru
Get-Service OpenVPNService| Start-Service
Open the network connections dialog (ncpa.cpl) and make sure that OpenVPN Wintun virtual adapter is now enabled. If it is not, check the log file C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\log\server.log.
Options error: In C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config-auto\server.ovpn:1: Maximum option line length (256) exceeded, line starts with…
Change line break character to Windows CRLF (in Notepad++, select Edit -> EOL Conversion -> Windows CR LF) in server.ovpn. Save the file and restart the OpenVPNService.
This OpenVPN configuration allows remote clients to access the server resources only. Other computers and services in the server‘s local network are not available for remote clients. In order to allow OpenVPN clients to access the internal LAN, enable the IPEnableRouter option in the registry (enables IP routing in Windows including routing between Hyper-V networks, and allows you to use port-forwarding):
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters" /v IPEnableRouter /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
Add the routes to your local IP network to the server configuration file:
push "route 10.24.1.0 255.255.255.0" push "route 192.168.31.0 255.255.255.0"
If needed, assign DNS server addresses to the client:
push "dhcp-option DNS 192.168.31.10" push "dhcp-option DNS 192.168.31.11"
If you want to redirect all client requests (including the Internet traffic) to your OpenVPN server, add the option:
push "redirect-gateway def1"
Configuring OpenVPN Client on Windows
Create a template configuration file for a VPN client (based on client.ovpn template) on your server with the following settings (the file name is testuser1.ovpn):
client dev tun proto udp remote your_vpn_server_address 1194 resolv-retry infinite nobind persist-key persist-tun ca ca.crt cert testuser1.crt key testuser1.key remote-cert-tls server tls-auth ta.key 1 cipher AES-256-GCM connect-retry-max 25 verb 3
Download and install OpenVPN Connect for Windows (https://openvpn.net/downloads/openvpn-connect-v3-windows.msi).
Then copy the following files from your server to the computer with the installed OpenVPN client:
- ca.crt
- testuser1.crt
- testuser1.key
- dh.pem
- ta.key
- testuser1.ovpn
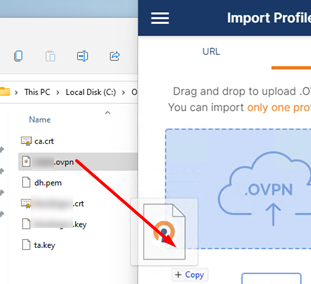
Import *.ovpn profile file and try to connect to your VPN server.
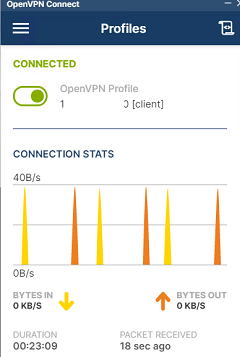
If you have set it correctly, you will see the image below:
Check the OpenVPN connection log on the client: C:\Program Files\OpenVPN Connect\agent.log
Mon Jul 17 08:09:30 2022 proxy_auto_config_url
Mon Jul 17 08:09:31 2022 TUN SETUP
TAP ADAPTERS:
guid='{25EE4A55-BE90-45A0-88A1-8FA8FEF24C42}' index=22 name='Local Area Connection'
Open TAP device "Local Area Connection" PATH="\\.\Global\{25EE4A55-BE90-45A0-88A1-8FA8FEF24C42}.tap" SUCCEEDED
TAP-Windows Driver Version 9.24
ActionDeleteAllRoutesOnInterface iface_index=22
netsh interface ip set interface 22 metric=1
Ok.
netsh interface ip set address 22 static 10.24.1.10 255.255.255.252 gateway=10.24.1.5 store=active
IPHelper: add route 10.24.1.1/32 22 10.24.1.5 metric=-1The client has successfully connected to the VPN server and received the IP address 10.24.1.10.
Now check the OpenVpn log on the server-side (C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\log\openvpn.log). Here you can also see that the client with the testuser1 certificate has successfully connected to the server.
2022-07-17 08:09:35 192.168.13.20:55648 [tesuser1] Peer Connection Initiated with [AF_INET6]::ffff:192.168.13.20:55648 2022-07-17 08:09:35 tesuser1/192.168.13.20:55648 MULTI_sva: pool returned IPv4=10.24.1.10, IPv6=(Not enabled) 2022-07-17 08:09:35 tesuser1/192.168.13.20:55648 MULTI: Learn: 10.24.1.10 -> testuser1/192.168.13.20:55648 2022-07-17 08:09:35 tesuser1/192.168.13.20:55648 MULTI: primary virtual IP for tesuser1/192.168.13.20:55648: 10.24.1.10
10 comments
Hello,
thanks for the detailed guide.
in which step did you create “testuser1.crt”
its mentioned twice once in the files we need to move along with the OVPN file and inside the openvpn config file itself, but you didn’t generate it in the guide?
Create .req and .key
./easyrsa gen-req testuser1 nopassThen run the following to create and sign a .crt file.
./easyrsa sign-req client testuser1Hi, thanks for a great guide!
Following up on the same question, I get:
C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\bin>./easyrsa gen-req testuser1 nopass
‘.’ is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.
Not sure if I understood what to do there. Can you please write the step for dummies LOL?
can this be installed on windows server 2008 r2
I haven’t tested OpenVPN servers on WS 2008 in production, but I don’t think there will be any issues with it.
Hi!
Thank you for the guide. It is way more readable than the documentation from OpenVPN 🙂
My OpenVPN Wintun virtual adapter is not enabled after folowing your steps.
The log says ” All tap-windows6 adapters on this system are currently in use or disabled.”
Do you know how to resolve this error? Disabling and re-enabling the driver doesn’t help and neither does restarting the PC and/or services.
Also i have a question:
I am installing the VPN on a Win10 machine in my home so that i can reach it at all times.
When specifying “your_vpn_server_address” in the client config, i suppose i should use my Homw Wi-Fi’s public IP?
And for that to work i would need to do some port forwarding, right?
Will this still be safe then?`
Thanks in advance!
_https://woshub.com/install-configure-openvpn-server-windows/#h2_4
works perfect. Execept to get WinTun pluged in I needed to reboot the server.
I was able to RDP to a mobile (4G) sim. For this project
_http://122.168.196.104/tramoret.html
Thanks anyways
Seems like web UI is not running with this set up, right?
Any why to have it run nevertheless?
Hi. Thanks for the great walkthrough.
I’m following it step-by-step on mg VPS running Windows 10, and everything is working great. However there’s a very small issue which makes the entire process being left useless.
When I add the config to my client, it gets connected without any issues. Both the server and the client logs are showing that the connection is established. But when I try to check my IP address on my client, it shows my public IP before the VPN connection. I tried playing with the config files but didn’t get any lucks. It either doesn’t connect at all, or it connects and my traffic is still going through my own public IP address.
I’ll be highly grateful if you can help me with this.
If you want to send all the packets from your computer into the VPN tunnel, then you need to add the following option to the client’s config file
push "redirect-gateway def1"