By default, regular (non-admin) users cannot manage Windows services. This means that users cannot stop, start, restart, or change the settings and permissions of Windows services. In some cases, it is necessary for a user to have permission to restart or manage certain services. In this article, we’ll look at several ways to manage the permissions for Windows services. As an example, we’ll show how to allow a non-admin user to restart a specific Windows service.
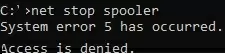
Suppose you need to give the domain account contoso\tuser the right to restart the Print Spooler service. If the non-admin user tries to restart the service, an error will be displayed:
net stop spooler
System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied.
In Windows, there are several ways to grant service permissions:
Manage Service Permission with Windows CMD
You can use the built-in sc.exe (Service Controller) console command to manage the permissions of a Windows service.
sc show— list current service permissionssc sdset– change service permissions
The main disadvantage of this method is that the format for the granting of rights to the service is very complicated. Security Description Definition Language (SDDL) format is used.
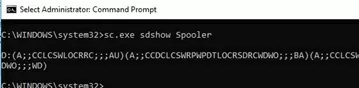
You can get the current service permissions as an SDDL string:
sc.exe sdshow Spooler
D:(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;AU)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)
(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)S:(AU;FA;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;WD)
What are all these symbols?
S: — System Access Control List (SACL) D: — Discretionary ACL (DACL)
The first letter after brackets means: allow (A) or deny (D).
Assignable permissions are the next set of characters.
CC — SERVICE_QUERY_CONFIG (query service settings) LC — SERVICE_QUERY_STATUS (get service status) SW — SERVICE_ENUMERATE_DEPENDENTS LO — SERVICE_INTERROGATE CR — SERVICE_USER_DEFINED_CONTROL RC — READ_CONTROL RP — SERVICE_START WP — SERVICE_STOP DT — SERVICE_PAUSE_CONTINUE
The last 2 characters are the objects (user, group, or SID) to which permissions are granted. Here is a list of predefined groups.
AU Authenticated Users AO Account operators RU Alias to allow previous Windows 2000 AN Anonymous logon AU Authenticated users BA Built-in administrators BG Built-in guests BO Backup operators BU Built-in users CA Certificate server administrators CG Creator group CO Creator owner DA Domain administrators DC Domain computers DD Domain controllers DG Domain guests DU Domain users EA Enterprise administrators ED Enterprise domain controllers WD Everyone PA Group Policy administrators IU Interactively logged-on user LA Local administrator LG Local guest LS Local service account SY Local system NU Network logon user NO Network configuration operators NS Network service account PO Printer operators PS Personal self PU Power users RS RAS servers group RD Terminal server users RE Replicator RC Restricted code SA Schema administrators SO Server operators SU Service logon user
You can use pre-defined groups in the DACL, or you can specify any user or group by SID. Use the command to get the SID for the current user:
whoami /user
Or, you can use the Get-ADUser cmdlet to find the SID for any domain user:
Get-ADUser -Identity 'sadams' | select SID
Use the Get-ADGroup cmdlet to get the domain group SID:
Get-ADGroup -Filter {Name -eq "ny-ithelpdesk"} | Select SID
To assign an SDDL string with permissions to a specific service, use the sc sdset command. In this example, add the following line to the service ACL.
(A;;RPWPCR;;;S-1-5-21-2133228432-2794320136-1823075350-1000)
- A – Allow
- RPWPCR – RP (SERVICE_START) + WP (SERVICE_STOP) + CR ( SERVICE_USER_DEFINED_CONTROL)
- SID – user or group SID
Add your ACL to the end of the string returned by sdshow. Use the sc sdset command to apply the new permissions to a service:
sc sdset Spooler "D:(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;AU)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;RPWPCR;;;S-1-5-21-2133228432-2794320136-1823075350-1000)"
If you have a valid DACL, the command will return:
[SC] SetServiceObjectSecurity SUCCESS
If you have specified a non-existent SID or made a mistake in the SDDL syntax, an error will occur:
No mapping between account names and security IDs was done.
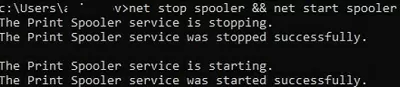
Check that the non-admin user can now stop and start the service:
net stop spooler && net start spooler
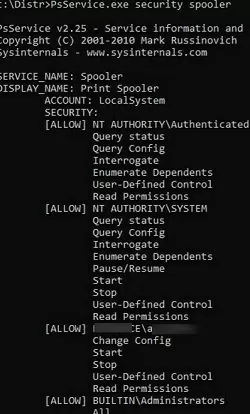
A more convenient way to view the current list of service permissions is to use the psservice.exe tool (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/psservice):
psservice.exe security spooler
SERVICE_NAME: Spooler
DISPLAY_NAME: Print Spooler
ACCOUNT: LocalSystem
SECURITY:
[ALLOW] NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users
Query status
Query Config
Interrogate
Enumerate Dependents
User-Defined Control
Read Permissions
[ALLOW] NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Query status
Query Config
Interrogate
Enumerate Dependents
Pause/Resume
Start
Stop
User-Defined Control
Read Permissions
[ALLOW] WOSHUB\max_adm
Change Config
Start
Stop
User-Defined Control
Read Permissions
[ALLOW] BUILTIN\Administrators
All
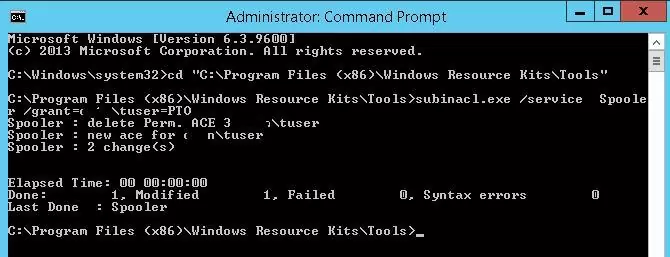
To allow the contoso\tuser user account to restart the service:
subinacl.exe /service Spooler /grant=contoso\tuser=PTO
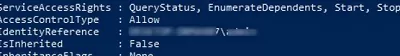
In this case, the user has been granted the permissions to Pause/Continue, Start, and Stop the service. Complete list of available privileges:
F : Full Control R : Generic Read W : Generic Write X : Generic eXecute L : Read controL Q : Query Service Configuration S : Query Service Status E : Enumerate Dependent Services C : Service Change Configuration T : Start Service O : Stop Service P : Pause/Continue Service I : Interrogate Service U : Service User-Defined Control Commands
To revoke a user’s assigned rights to a service, use the /revoke option:
subinacl.exe /service Spooler /revoke=contoso\tuser
However, SubInACL is not currently available for download from the Microsoft website and is not recommended for use.
How to Change Service Permission Using Process Explorer
You can manage service permissions from the GUI using the Process Explorer tool (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/process-explorer).
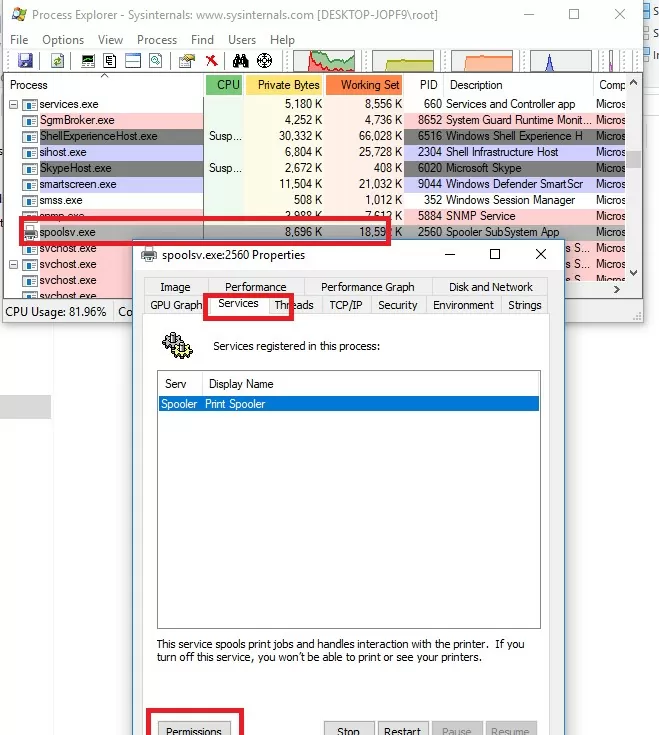
- Run the Process Explorer as an administrator and look for the process of the service that you need in the list of processes. In this example it is
spoolsv.exe(the spooler executable C:\Windows\System32\spoolsv.exe). Open the process properties and go to the Services tab; - Click on the Permissions button. The current ACL of the service appears in the window. By default, local users can only view (read) the service state;
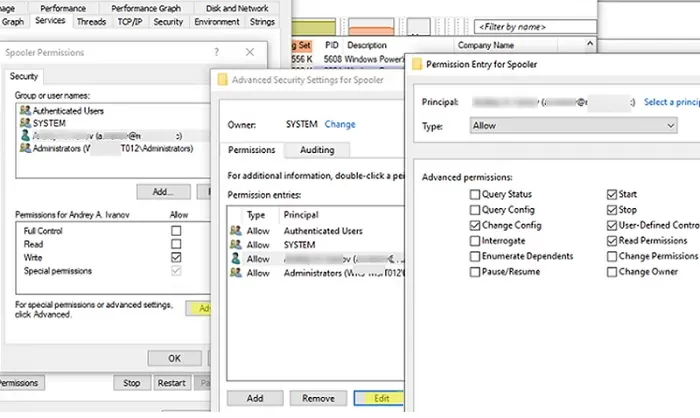
- Add the user or group you want to grant service permissions. By default only the following service permissions are available: Full Control, Write, and Read;
- You can assign Write permission to a service so that users can start and stop it. However, this also allows the user to change or even remove the service;
- To allow only the start/stop of the service, click on the Advanced button -> select your user, click on Edit -> click on Show Advanced Permissions. Leave only Start, Stop, Read, Query Status, and Custom Control options in the permissions list;
- Save changes;
- The assigned user can now restart the service.
Set Service Permissions Using PowerShell
The built-in Set-Service service management cmdlet allows you to set the permissions on a service using the SDDL format, similar to sc sdset:
$SDDL = "D:(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;AU)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;RPWPCR;;;S-1-5-21-2133228432-2794320136-1823075350-1000)"
Set-Service -Name Spooler -SecurityDescriptorSddl $SDDL
In Windows PowerShell 5.1, this command fails:
Set-Service : A parameter cannot be found that matches parameter name 'SecurityDescriptorSddl'.
You can also manage permissions on various Windows objects using the Carbon module from the PowerShell Gallery. Install the module:
Install-Module -Name 'Carbon'
Import-Module 'Carbon'
In order to grant permissions to the service, use the command:
Grant-CServicePermission -Identity woshub\maxadm -Name spooler -QueryStatus -EnumerateDependents -Start -Stop
List the service’s current ACL:
Get-ServicePermission -Name spooler|fl
How to Use Group Policy to Grant the Permissions for a Service
If you need to grant users permission to start and stop the service on all domain servers or computers, the easiest way to do this is to use the Group Policy (GPO) features.
- Create a new GPO or edit the existing one and link it to the necessary Active Directory container (OU) with the computer objects. Go to Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services;
- Locate the Print Spooler service and open its properties;
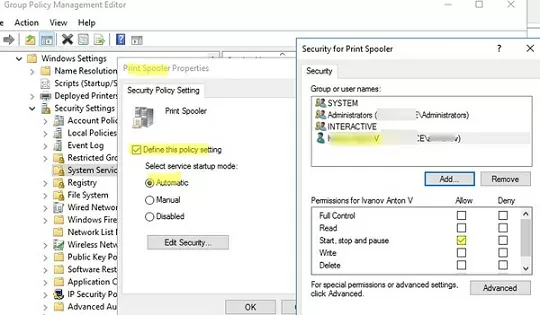
- Enable the Define this policy settings option, enable auto-start for the service, and click Edit Security;
- In the service security settings, add the user or domain group that you want to assign permissions to the service. Grant Start, stop and pause and Read permission;
- All you need to do is wait for the Group Policy settings to be updated on the client computers and check that your user can now restart the service.
The security settings for all services for which you changed the default permissions are stored in their own registry key HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\<servicename>\Securityin the Security parameter (REG_BINARY type).
This means that one of the ways to set the same permissions on other computers is to export/import this registry parameter. You can use the GPO to deploy changes to the registry on domain computers.
If you want the user to be able to stop/start/restart the service remotely (without granting them local sign-in permissions or RDP access), you need to allow them to remotely enumerate the Service Control Manager service (scmanager).
The following command allows the remote group (user) with the specified SID to enumerate the list of services on the remote computer:
sc sdset scmanager "D:(A;;CC;;;AU)(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;SU)(A;;CCLCRPWPRC;;;SY)(A;;KA;;;BA)(A;;CC;;;AC)(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;{PASTE_YOUR_SID_HERE})S:(AU;FA;KA;;;WD)(AU;OIIOFA;GA;;;WD)"
Otherwise, you will get an error when you try to query services on the remote Windows host:
sc \\lonts-01 query
[SC] OpenSCManager FAILED 5: Access is denied.
So we have looked at a number of different ways of managing permissions to Windows services that allow granting non-admin users any permissions for system services.
14 comments
How to Grant non-Administrators Rights like remote desktop users to Install softwares only and allow running softwares which demands admin permission to run the software ?
You can easily grant non-administrators the ability to manage services with System Frontier. The RBAC model is very flexible, but easy to manage through a single web interface.
The SubInACL Tool worked perfectly for my needs. I have one non-admin user who needs to restart a single service occasionally. Problem solved. Thanks!
Many thank, very usefull, I used Security Template procedure to definetly disable the new service (Windows Update Medic Service) in Windows 10 Pro! Finally!
when granting a non-administrator the rights to start/stop/query a service as described above, if they do, does it change the ‘LogOnAs’ attribute for the service? The services I am exposing must also access network resources, to which the non-admin users will NOT have access. Would the above break this use case?
[…] Possibly this How to Allow Non-Admin Users to Start/Stop Windows Service? | Windows OS Hub […]
Just used the first method at the top adding (A;;RPWPCR;;;RD) for remote access users to restart a service. Thanks for the help!
[…] WindowsOSHub – How to Allow Non-Admin Users to Start/Stop Windows Service? […]
The only method that worked in our environment was using process explorer.
In my opinion, it’s also the easiest.
Thank you!
How to grant users rights to manage services:
_https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/windows-security/grant-users-rights-manage-services
Thank you!
subinacl doesn’t officially exist anymore. I wonder when will Microsoft deprecate commands like “dir”…
So we can allow non-admins to restart the service, but services won’t restart in CMD or PowerShell without running those as administrator, so we can’t have a shortcut to restart the service?
just discovered that adding permissions to services seems to only be not working on Windows Server 2019 Servers. It works just fine on Windows Server 2012 R2 Servers. I am not sure whether or not Windows 2016 Servers are affected.
If anyone has any information on how to add permissions for non-admins to remotely start/stop services on a Windows 2019 Server, please let me know.
UPD:
Solution for Server 2019 specific problem with assigning access to SCManager
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control /v RemoteAccessExemption /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
Credit to tadmaz-quad for posting the question and the answer – Thanks !!
https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/a9b38117-1e98-4a9e-a4d8-7bbbc3ace2f2/remotely-stopstart-services-not-working-for-nonadmins?forum=ws2019
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4457739/blocking-remote-callers-from-starting-or-stopping-services-when-they-a