This guide should help you to migrate (move) Remote Desktop Connection Broker and RDS Web Access roles to another server. In this example, we will migrate the RDS Connection Broker role from Windows Server 2012 R2 host to Windows Server 2019. We will also look at the specifics of migrating the RD Web Access role.
Some compatibility restrictions of Windows Server versions in an RDS farm:
- When updating a Windows Server version, start with the host with the RD Connection Broker role;If you are using the high-availability RD Connection Broker deployment, it is enough to leave one host with the Connection Broker role in a cluster, perform an in-place upgrade of the Windows Server version, then upgrade other hosts, and add them to the cluster.
- A terminal farm can contain RDSH hosts with different Windows Server versions (2019/2016/2012R2). It is recommended to use hosts with the same version of Windows Server within the same RDS collection. This means that you may create two RDS collections, for example, one with Windows Server 2019 hosts, and another one with Windows Server 2012 R2 hosts;
- RDS hosts with previous Windows Server versions can use a Connection Broker with a newer version of OS (for example, RDS hosts running WS2012R2 or WS2016 can use RD Connection Broker with WS2019, but not vice versa).
- When upgrading the Windows Server version on RDSH hosts, be sure to install the RDS Licensing server on the latest version of Windows Server and activate new RDS CALs.
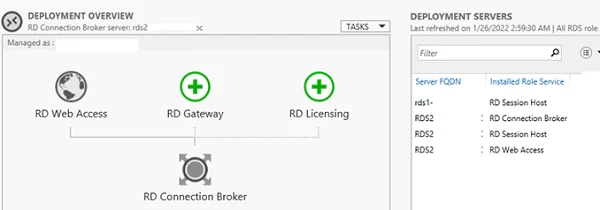
In my case, two RDS hosts are running Windows Server 2012 R2:
Rds2– with the RD Connection Broker, Web Access, and RDSH rolesRds1– with the RDSH role
You can list roles in your RDS deployment with Server Manager or PowerShell:
Get-RDServer
The task is to migrate the Connection Broker role with the configured RemoteApp and RDS collections to a new Windows Server 2019 host (an in-place upgrade is not applicable).
Prepare a new host with Windows Server 2019 and install the RD Connection Broker and RD Licensing roles (if needed) on it.
Windows Server doesn’t have built-in tools to easily transfer configured RDS roles between hosts.
To export/import current RDCB settings, you can use the ExportImportRdsDeployment module from PowerShell Gallery.
C:\Windows\rdcbDb\).Install the ExportImportRdsDeployment module from PowerShell Gallery (you can also install a PowerShell module offline):
Install-Module ExportImportRdsDeployment -Force
Import-Module ExportImportRdsDeployment
Install-Module : The term 'Install-Module' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.
Download and install KB3191564 (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54616) to update your PowerShell version to 5.1.
If you receive an Install-Module: Unable to download from URI error when running the command, you need to enable the TLS 1.2 protocol for the PowerShell connection:
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
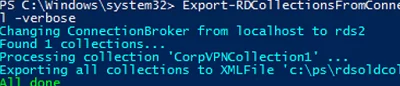
Export the RDS collections to an XML file:
Export-RDCollectionsFromConnectionBroker -ConnectionBroker localhost –XMLFile c:\ps\rdsoldcol.xml –verbose
Then export your RDS configuration (including a list of servers in deployment):
Export-RDDeploymentFromConnectionBroker -ConnectionBroker localhost –XMLFile c:\ps\rdsdeployment.xml -Verbose
If you are using wildcard certificates on your old RDS server, export them in PFX (with a password).
Copy both files to your new RDS server running Windows Server 2019. Also, install the module:
Install-Module ExportImportRdsDeployment -Force
In this example, I am migrating the RDS configuration without certificates, so I have specified files that do not exist. If you are using certificates in RDS deployment, provide your file paths and password.
Then run the following commands:
$RDGatewayCertPath = "C:\\PS\\nocert.pfx"
$RDWebAccessCertPath = "C:\\PS\\nocert.pfx"
$RDRedirectorCertPath = "C:\\PS\\nocert.pfx"
$RDPublishingCertPath = "C:\\PS\\nocert.pfx "
$RDGatewayCertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "nopass" -AsPlainText -Force
$RDWebAccessCertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "nopass" -AsPlainText -Force
$RDRedirectorCertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "nopass" -AsPlainText -Force
$RDPublishingCertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "nopass" -AsPlainText -Force
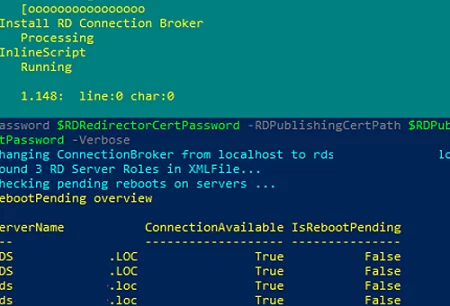
Import-RDDeploymentToConnectionBroker -ConnectionBroker localhost -XmlFile c:\ps\rdsdeployment.xml -RDGatewayCertPath $RDGatewayCertPath -RDGatewayCertPassword $RDGatewayCertPassword -RDWebAccessCertPath $RDWebAccessCertPath -RDWebAccessCertPassword $RDWebAccessCertPassword -RDRedirectorCertPath $RDRedirectorCertPath -RDRedirectorCertPassword $RDRedirectorCertPassword -RDPublishingCertPath $RDPublishingCertPath -RDPublishingCertPassword $RDPublishingCertPassword -Verbose
If you are not using certificates for RDS, you will see a warning that the files were not found. Ignore this error.
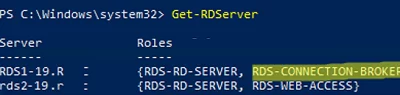
Run the Get-RDServer command and make sure that the RD Connection Broker role is on a new server.
Import the RDS collections:
Import-RDCollectionsToConnectionBroker -ConnectionBroker localhost -XmlFile "C:\PS\rdsoldcol.xml" -Verbose
Make sure that all RD collections with the configured permissions and Remote Apps appeared in the RDS management console.
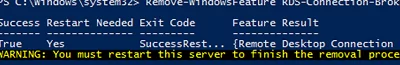
Remove the RDCB role on the previous WS2012R2 host using Server Manager or the Remote-WindowsFeature command:
Remove-WindowsFeature RDS-Connection-Broker
There are some nuances when migrating a configured RD Web Access role. If you are moving the RDWebAccess role between different Windows Server versions (with different IIS versions), you will have to copy the settings manually.
- Install the RDS-Web-Access role and add a new server to your RDS farm:
Install-WindowsFeature RDS-Web-Access - Import the certificates (if needed);
- You can use Microsoft Web Deploy v3.6 to copy RDWeb site settings between servers with the same Windows Server versions. Download and install the WebDeploy_amd64_en-US package (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=43717) on both hosts;
- To transfer IIS site settings offline, you can use the commands below:
cd "C:\Program Files (x86)\IIS\Microsoft Web Deploy V3"On a source host:msdeploy -verb:sync -source:apphostconfig="Default Web Site" -dest:archivedir=c:\ps\rdwebOn a target host:msdeploy -verb:sync -source:archivedir=c:\ps\rdweb -dest:appHostConfig="Default Web Site"You can also use IIS backup features.
- Install the RDS-Web-Access role and add a new server to your RDS farm:
Make sure that your custom IIS settings have been applied (including your expired password change form for RD Web Access). Similarly, you can migrate the Remote Desktop Gateway role.
If the URL address of your RD Web Access server has changed, be sure to change it in the RDS Single Sign-On policy.
2 comments
Excuse me if this is a dumb question. In an HA environment with existing 2012 R2 broker servers, can the 2019 Server(s) be simply added and then inherit the RDS configurations? Then make one of the 2019 Servers the active connection broker, followed by removing the 2012 R2 servers?
Yes, same idea, this would be an easy and smooth way for migrating the role