In this article, we will show how to disable legacy versions of the Transport Layer Security protocol in Windows using Group Policies. TLS 1.0 and 1.1 versions are no longer secure and should be disabled by default for all services. If you have migrated all your services to TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3, you can disable support for the legacy protocol on your Windows clients and servers using GPO.
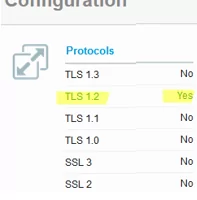
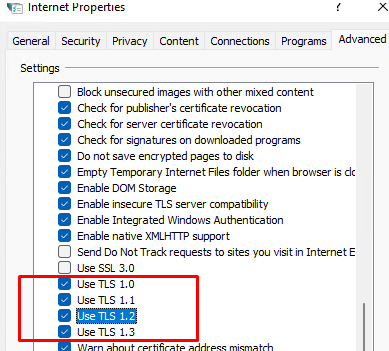
On Windows client, you can view a list of enabled TLS protocol versions for a browser in the Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl). This screenshot shows that TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, and TLS 1.3 are enabled. When establishing a connection to a server, the highest TLS version supported by both a client and a server is selected for encryption.
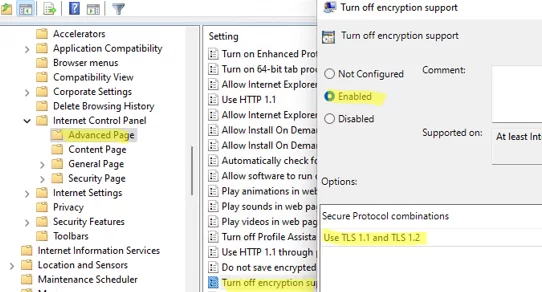
You can set a list of TLS/SSL protocols enabled in the Internet Options tab on a client using the Turn Off Encryption Support GPO option under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Explorer Control Panel -> Advanced Page.
Enable the policy and select which TLS/SSL versions your users will be allowed to use in the Secure Protocol combinations dropdown list.
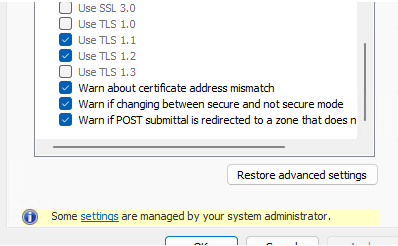
You will have to restart your computer to apply new GPO settings, Open Internet Options again and make sure that only those TLS versions are available that you have allowed in GPO. The user won’t be able to change these settings (note Some settings are managed by your system administrator message).
Unfortunately, you cannot leave only TLS 1.3 and TLS 1.2 enabled here, since there is no such option in GPO. Also, it doesn’t disable TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 support on the side of your Windows Server (in IIS or Exchange, for example).
So, it is better to disable legacy TLS versions directly through the registry. You can use the GPO to deploy registry parameters you need to domain computers.
In order to disable TLS 1.0 on Windows both for a client and a server, add the following options to the registry:
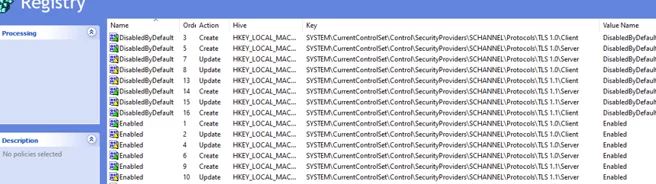
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client] "DisabledByDefault"=dword:00000001 "Enabled"=dword:00000000 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server] "DisabledByDefault"=dword:00000001 "Enabled"=dword:00000000
You can disable other protocols In the same way. It is enough to replace the highlighted path in the registry with SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0, TLS 1.1, etc.
To force enable TLS 1.2, add the registry entries below:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client] "DisabledByDefault"=dword:00000000 "Enabled"=dword:00000001 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server] "DisabledByDefault"=dword:00000000 "Enabled"=dword:00000001
Thus. you will see the following in the Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry section of GPO.
Restart Windows to apply settings.
Besides changing the settings of available TLS versions in the registry, you need to allow using TLS 1.2 for NET 3.5 and 4.x apps, and for WinHTTP. For example, Outlook is using encryption settings for WinHTTP (learn more in this article).
To enable system encryption protocols for .Net 3.5 and 2.0:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727] "SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727] "SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727] "SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727] "SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
For .Net 4.x:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319] "SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319] "SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
To enable using TLS 1.2 for WinHTTP:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\WinHttp] "DefaultSecureProtocols"=dword:00000800 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\WinHttp] "DefaultSecureProtocols"=dword:00000800
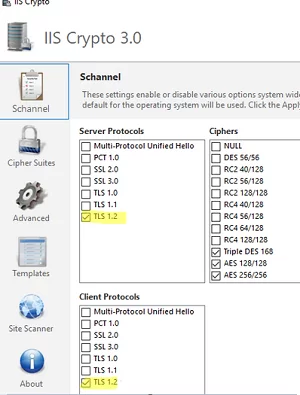
On Windows Server, you can also use the ISS Crypto GUI tool (https://www.nartac.com/Products/IISCrypto/Download) to view and configure SCHANNEL settings.